MUC17 Is a Potential New Prognostic Biomarker and Promotes Pancreatic Cancer Progression in Obstructive Jaundice
- PMID: 39396510
- PMCID: PMC12324704
- DOI: 10.1159/000541874
MUC17 Is a Potential New Prognostic Biomarker and Promotes Pancreatic Cancer Progression in Obstructive Jaundice
Abstract
Introduction: Our working group has previously shown that bile acids (BAs) accelerate carcinogenic processes in pancreatic cancer (PC) in which mucin 4 (MUC4) expression has a central role. However, the role of other mucins in PC is less clear, especially in bile-induced cancer progression. The study aim was to investigate expression of MUC17 in BA- or human serum-treated pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) cell lines.
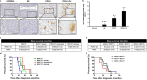
Methods: Different cell-based assays with RNA silencing/overexpression were used to study the role of MUC17 in cancer progression. Protein expression of MUC17 was evaluated in 55 human pancreatic samples by immunohistochemistry, and Kaplan-Meier survival analysis was used to compare survival curves.
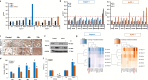
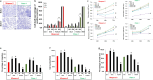
Results: Expression of MUC17 increased in PDAC patients, especially in obstructive jaundice (OJ), and the elevated MUC17 expression associated with poorer overall survival (10.66 ± 1.99 vs. 15.05 ± 2.03 months; log-rank: 0.0497). Treatment of Capan-1 and AsPC-1 cells with BAs or with human serum obtained from PDAC + OJ patients enhanced the expression of MUC17, as well as the proliferative potential of the cells, whereas knockdown of MUC17 alone or in combination with MUC4 decreased BAs-induced carcinogenic processes.
Conclusion: Our results demonstrated that MUC17 has a central role in bile-induced PC progression, and in addition to MUC4, this isoform also can be used as a novel prognostic biomarker.
Keywords: Bile acids; MUC17; MUC4; Obstructive jaundice; Pancreatic cancer.
© 2024 The Author(s). Published by S. Karger AG, Basel.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures




References
-
- Huang J, Lok V, Ngai CH, Zhang L, Yuan J, Lao XQ, et al. Worldwide burden of, risk factors for, and trends in pancreatic cancer. Gastroenterology. 2021;160(3):744–54. - PubMed
-
- Corfield AP. Mucins: a biologically relevant glycan barrier in mucosal protection. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015;1850(1):236–52. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

