Biology of human respiratory syncytial virus: Current perspectives in immune response and mechanisms against the virus
- PMID: 39396572
- PMCID: PMC11513633
- DOI: 10.1016/j.virusres.2024.199483
Biology of human respiratory syncytial virus: Current perspectives in immune response and mechanisms against the virus
Abstract
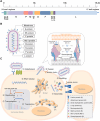
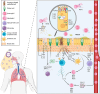
Human respiratory syncytial virus (hRSV) remains a leading cause of morbidity and mortality in infants, young children, and older adults. hRSV infection's limited treatment and vaccine options significantly increase bronchiolitis' morbidity rates. The severity and outcome of viral infection hinge on the innate immune response. Developing vaccines and identifying therapeutic interventions suitable for young children, older adults, and pregnant women relies on comprehending the molecular mechanisms of viral PAMP recognition, genetic factors of the inflammatory response, and antiviral defense. This review covers fundamental elements of hRSV biology, diagnosis, pathogenesis, and the immune response, highlighting prospective options for vaccine development.
Keywords: Current vaccines against hRSV; Immune response; Pathogenesis; Viral diagnosis; hRSV.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

