Evaluation of Minimum-to-Severe Global and Macrovesicular Steatosis in Human Liver Specimens: A Portable Ambient Light-Compatible Spectroscopic Probe
- PMID: 39396823
- PMCID: PMC11614560
- DOI: 10.1002/jbio.202400292
Evaluation of Minimum-to-Severe Global and Macrovesicular Steatosis in Human Liver Specimens: A Portable Ambient Light-Compatible Spectroscopic Probe
Abstract
Background and aims: Hepatic steatosis (HS), particularly macrovesicular steatosis (MaS), influences transplant outcomes. Accurate assessment of MaS is crucial for graft selection. While traditional assessment methods have limitations, non-invasive spectroscopic techniques like Raman and reflectance spectroscopy offer promise. This study aimed to evaluate the efficacy of a portable ambient light-compatible spectroscopic system in assessing global HS and MaS in human liver specimens.
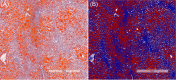
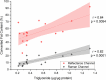
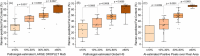
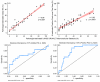
Methods: A two-stage approach was employed on thawed snap-frozen human liver specimens under ambient room light: biochemical validation involving a comparison of fat content from Raman and reflectance intensities with triglyceride (TG) quantifications and histopathological validation, contrasting Raman-derived fat content with evaluations by an expert pathologist and a "Positive Pixel Count" algorithm. Raman and reflectance intensities were combined to discern significant (≥ 10%) discrepancies in global HS and MaS.
Results: The initial set of 16 specimens showed a positive correlation between Raman and reflectance-derived fat content and TG quantifications. The Raman system effectively differentiated minimum-to-severe global and macrovesicular steatosis in the subsequent 66 specimens. A dual-variable prediction algorithm was developed, effectively classifying significant discrepancies (> 10%) between algorithm-estimated global HS and pathologist-estimated MaS.
Conclusion: Our study established the viability and reliability of a portable spectroscopic system for non-invasive HS and MaS assessment in human liver specimens. The compatibility with ambient light conditions and the ability to address limitations of previous methods marks a significant advancement in this field. By offering promising differentiation between global HS and MaS, our system introduces an innovative approach to real-time and quantitative donor HS assessments. The proposed method holds the promise of refining donor liver assessment during liver recovery and ultimately enhancing transplantation outcomes.
© 2024 The Author(s). Journal of Biophotonics published by Wiley‐VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors H.G., A.B.T., H.Z., I.P.J.A., and K.C.H. have filed a PCT (the Patent Cooperation Treaty) application, and they stand to benefit should the patent be awarded in the national phase.
Figures


References
-
- Linares I., Hamar M., Selzner N., and Selzner M., “Steatosis in Liver Transplantation: Current Limitations and Future Strategies,” Transplantation 103 (2019): 78–90. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

