Efficient Treatment of Psoriasis Using Conditioned Media from Mesenchymal Stem Cell Spheroids Cultured to Produce Transforming Growth Factor- β 1-Enriched Small-Sized Extracellular Vesicles
- PMID: 39396918
- PMCID: PMC11612221
- DOI: 10.15283/ijsc24089
Efficient Treatment of Psoriasis Using Conditioned Media from Mesenchymal Stem Cell Spheroids Cultured to Produce Transforming Growth Factor- β 1-Enriched Small-Sized Extracellular Vesicles
Abstract
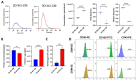
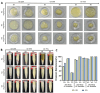
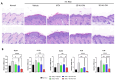
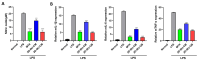
Psoriasis is a common chronic inflammatory disease in which keratinocytes proliferate abnormally due to excessive immune action. Psoriasis can be associated with various comorbidities and has a significant impact on health-related quality of life. Although many systemic treatments, including biologic agents, have been developed, topical treatment remains the main option for psoriasis management. Consequently, there is an urgent need to develop topical treatments with minimal side effects and high efficacy. Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) exhibit excellent immune regulation, anti-inflammatory activities, and therapeutic effects, and MSC-derived extracellular vesicles (EVs) can serve as crucial mediators of functional transfer from MSCs. Therefore, this study aimed to develop a safe and easy-to-use emulsion cream for treating psoriasis using MSC conditioned media (CM) containing EVs. We developed an enhanced Wharton's jelly MSC (WJ-MSC) culture method through a three-dimensional (3D) culture containing exogenous transforming growth factor-β3. Using the 3D culture system, we obtained CM from WJ-MSCs, which yielded a higher EV production compared to that of conventional WJ-MSC culture methods, and investigated the effect of EV-enriched 3D-WJ-MSC-CM cream on psoriasis-related inflammation. Administration of the EV-enriched 3D-WJ-MSC-CM cream significantly reduced erythema, thickness, and scaling of skin lesions, alleviated imiquimod-induced psoriasiform lesions in mice, and ameliorated histopathological changes in mouse skin. The upregulated mRNA expression of inflammatory cytokines, including IL-17a, IL-22, IL-23, and IL-36, decreased in the lesions. In conclusion, we present here a new topical treatment for psoriasis using an MSC EV-enriched cream.
Keywords: Emulsions; Extracellular vesicles; Immunomodulation; Mesenchymal stem cells; Psoriasis.
Conflict of interest statement
Ssang-Goo Cho is the CEO and CTO of StemExOne Co., Ltd. MS, KML, KS, GHK, and SJK are employed by StemExOne Co., Ltd. The other authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Extracellular Vesicles from Wharton's Jelly Mesenchymal Stem Cells Suppress CD4 Expressing T Cells Through Transforming Growth Factor Beta and Adenosine Signaling in a Canine Model.Stem Cells Dev. 2019 Feb 1;28(3):212-226. doi: 10.1089/scd.2018.0097. Epub 2019 Jan 14. Stem Cells Dev. 2019. PMID: 30412034
-
Effect of human Wharton's jelly mesenchymal stem cell paracrine signaling on keloid fibroblasts.Stem Cells Transl Med. 2014 Mar;3(3):299-307. doi: 10.5966/sctm.2013-0120. Epub 2014 Jan 16. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2014. PMID: 24436441 Free PMC article.
-
Engineered extracellular vesicles carrying let-7a-5p for alleviating inflammation in acute lung injury.J Biomed Sci. 2024 Mar 19;31(1):30. doi: 10.1186/s12929-024-01019-4. J Biomed Sci. 2024. PMID: 38500170 Free PMC article.
-
Characteristics and clinical applications of Wharton's jelly-derived mesenchymal stromal cells.Curr Res Transl Med. 2020 Jan;68(1):5-16. doi: 10.1016/j.retram.2019.09.001. Epub 2019 Sep 19. Curr Res Transl Med. 2020. PMID: 31543433 Review.
-
Therapeutic potential of mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles: A focus on inflammatory bowel disease.Clin Transl Med. 2024 Nov;14(11):e70075. doi: 10.1002/ctm2.70075. Clin Transl Med. 2024. PMID: 39488745 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

