Co-regulation and synteny of GFM2 and NSA2 links ribosomal function in mitochondria and the cytosol with chronic kidney disease
- PMID: 39396937
- PMCID: PMC11476648
- DOI: 10.1186/s10020-024-00930-8
Co-regulation and synteny of GFM2 and NSA2 links ribosomal function in mitochondria and the cytosol with chronic kidney disease
Abstract
Background: We previously reported aberrant expression of the cytosolic ribosomal biogenesis factor Nop-7-associated 2 (NSA2) in diabetic nephropathy, the latter also known to involve mitochondrial dysfunction, however the connections between NSA2, mitochondria and renal disease were unclear. In the current paper, we show that NSA2 expression is co-regulated with the GTP-dependent ribosome recycling factor mitochondrial 2 (GFM2) and provide a molecular link between cytosolic and mitochondrial ribosomal biogenesis with mitochondrial dysfunction in chronic kidney disease (CKD).
Methods: Human renal tubular cells (HK-2) were cultured (+/- zinc, or 5mM/20mM glucose). mRNA levels were quantified using real-time qPCR. Transcriptomics data were retrieved and analysed from Nakagawa chronic kidney disease (CKD) Dataset (GSE66494) and Kidney Precision Medicine Project (KPMP) ( https://atlas.kpmp.org/ ). Protein levels were determined by immunofluorescence and Western blotting. Cellular respiration was measured using Agilent Seahorse XF Analyzer. Data were analysed using one-way ANOVA, Students' t-test and Pearson correlation.
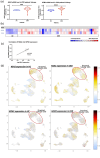
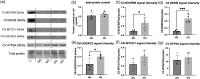
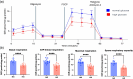
Results: The NSA2 gene, on human chromosome 5q13 was next to GFM2. The two genes were syntenic on opposite strands and orientation in multiple species. Their common 381 bp 5' region contained multiple transcription factor binding sites (TFBS) including the zinc-responsive transcription factor MTF1. NSA2 and GFM2 mRNAs showed a dose-dependent increase to zinc in-vitro and were highly expressed in proximal tubular cells in renal biopsies. CKD patients showed higher renal NSA2/GFM2 expression. In HK-2 cells, hyperglycaemia led to increased expression of both genes. The total cellular protein content remained unchanged, but GFM2 upregulation resulted in increased levels of several mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS) subunits. Furthermore, increased GFM2 expression, via transient transfection or hyperglycemia, correlated with decrease cellular respiration.
Conclusion: The highly conserved synteny of NSA2 and GFM2, their shared 5' region, and co-expression in-vitro and in CKD, shows they are co-regulated. Increased GFM2 affects mitochondrial function with a disconnect between an increase in certain mitochondrial respiratory proteins but a decrease in cellular respiration. These data link the regulation of 2 highly conserved genes, NSA2 and GFM2, connected to ribosomes in two different cellular compartments, cytosol and mitochondria, to kidney disease and shows that their dysregulation may be involved in mitochondrial dysfunction.
Keywords: Gene expression, diabetic nephropathy, chronic kidney disease, mitochondrial dysfunction; Mitochondria; NSA2; Protein synthesis; Ribosome biogenesis.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

