Serum lipidome reveals lipid metabolic dysregulation in severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome
- PMID: 39396989
- PMCID: PMC11472499
- DOI: 10.1186/s12916-024-03672-w
Serum lipidome reveals lipid metabolic dysregulation in severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome
Abstract
Background: Severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome (SFTS) is a rapidly progressing infectious disease with a high fatality rate caused by a novel bunyavirus (SFTSV). The role of lipids in viral infections is well-documented; however, the specific alterations in lipid metabolism during SFTSV infection remain elusive. This study aims to elucidate the lipid metabolic dysregulations in the early stages of SFTS patients.
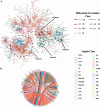
Methods: This study prospectively collected peripheral blood sera from 11 critical SFTS patients, 37 mild SFTS patients, and 23 healthy controls during the early stages of infection for lipidomics analysis. A systematic bioinformatics analysis was conducted from three aspects integrating lipid differential expressions, lipid differential correlations, and lipid-clinical indices correlations to reveal the serum lipid metabolic dysregulation in SFTSV-infected individuals.
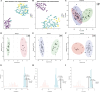
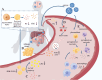
Results: Our findings reveal significant lipid metabolic dysregulation in SFTS patients. Specifically, compared to healthy controls, SFTS patients exhibited three distinct modes of lipid differential expression: increased levels of lipids including phosphatidylserine (PS), hexosylceramide (HexCer), and triglycerides (TG); decreased levels of lipids including lysophosphatidylcholine (LPC), acylcarnitine (AcCa), and cholesterol esters (ChE); and lipids showing "dual changes" including phosphatidylcholine (PC) and phosphatidylethanolamine (PE). Finally, based on lipid metabolic pathways and literature analysis, we systematically elucidated the potential mechanisms underlying lipid metabolic dysregulation in the early stage of SFTSV infection.
Conclusions: Our study presents the first global serum lipidome profile and reveals the lipid metabolic dysregulation patterns in the early stage of SFTSV infection. These findings provide a new basis for the diagnosis, treatment, and further investigation of the disease.
Keywords: Lipid; Lipidomics; Novel bunyavirus; SFTS.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Liu Q, He B, Huang SY, Wei F, Zhu XQ. Severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome, an emerging tick-borne zoonosis. Lancet Infect Dis. 2014;14(8):763–72. - PubMed
-
- Li H, Lu QB, Xing B, Zhang SF, Liu K, Du J, Li XK, Cui N, Yang ZD, Wang LY, et al. Epidemiological and clinical features of laboratory-diagnosed severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome in China, 2011–17: a prospective observational study. Lancet Infect Dis. 2018;18(10):1127–37. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

