Optimization of microwave parameters to enhance phytochemicals, antioxidants and metabolite profile of de-oiled rice bran
- PMID: 39397141
- PMCID: PMC11471765
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-74738-1
Optimization of microwave parameters to enhance phytochemicals, antioxidants and metabolite profile of de-oiled rice bran
Erratum in
-
Author Correction: Optimization of microwave parameters to enhance phytochemicals, antioxidants and metabolite profile of de-oiled rice bran.Sci Rep. 2025 Mar 25;15(1):10310. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-91310-7. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40133447 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
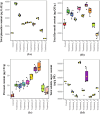
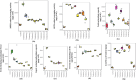
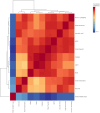
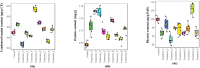
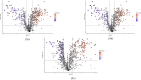
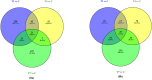
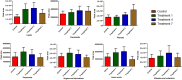
The current study explores the effects of microwave treatment at varying wattage and durations on the phytoconstituents, antioxidant status, anti-nutritional factors (ANFs), and metabolite profiles of de-oiled rice bran. The total phenolics and flavonoids showed both increases and decreases depending on specific microwave parameters, while flavonol content consistently increased across all treated groups compared to the control. The DPPH and ABTS free radical scavenging activity, total antioxidant capacity, FRAP, CUPRAC, metal chelating activity, and ascorbic acid content were enhanced in most of the microwaved samples; however, longer microwave exposure at higher wattage led to their reduction. A treatment-specific decrease in ANFs, including condensed tannins, oxalates, and phytates, was observed. HRMS-based untargeted metabolomics identified a diverse range of primary and secondary metabolites, which clustered in a group-specific manner, indicating notable group-wise metabolite variations. Analysis of discriminating metabolites revealed no significant differences in the overall levels of phenolics, flavonoids, vitamins and cofactors, sugars, amino acids, terpenoids, fatty acids, and their derivatives among the treated groups compared to the control; however, several individual metabolites within these metabolite classes differed significantly. These findings suggest that optimized microwaving of de-oiled rice bran can enhance phytochemicals and antioxidants while improving the metabolite profile.
Keywords: Antioxidants; De-oiled rice bran; High-resolution mass spectrometry (HRMS); Metabolomics; Microwave; Phytoconstituents.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Azrinnahar, M., Islam, N., Shuvo, A. A. S., Kabir, A. K. M. A. & Islam, K. M. S. Effect of feeding fermented (Saccharomyces cerevisiae) de-oiled rice bran in broiler growth and bone mineralization. J. Saudi Soc. Agric. Sci.20(7), 476–481. 10.1016/j.jssas.2021.05.006 (2021).
-
- Sunphorka, S., Chavasiri, W., Oshima, Y. & Ngamprasertsith, S. Protein and sugar extraction from rice bran and de-oiled rice bran using subcritical water in a semi-continuous reactor: Optimization by response surface methodology. Int. J. Food Eng.8(3). 10.1515/1556-3758.226 (2012).
-
- Ranjan, A., Kumar, S., Sahu, N. P., Jain, K. K. & Deo, A. D. Strategies for maximizing utilization of de-oiled rice bran (DORB) in the fish feed. Aquac. Int.30(1), 99–114. 10.1007/s10499-021-00791-6 (2022).
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

