Gingerol acts as a potent radiosensitizer in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma
- PMID: 39397185
- PMCID: PMC11471747
- DOI: 10.1007/s12672-024-01425-y
Gingerol acts as a potent radiosensitizer in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma
Abstract
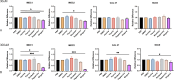
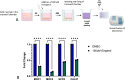
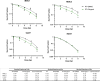
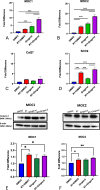
Treatment options for advanced head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) are limited and often cause severe toxicity and debilitating long-term impacts. Developing effective and safer treatments is warranted. Several plant extracts have shown their effectiveness, but a comprehensive comparison between plant extracts in HNSCC has not been reported. Our aim was to investigate the effect of different plant extracts on the proliferation and viability of HNSCC cell lines. In addition, we investigated the efficacy of combining cytotoxic plant extracts with radiation. Since RT is a cornerstone in the treatment and management of HNSCC, it is desirable to enhance its efficacy through combination with cytotoxic agents that have minimal side effects. HNSCC cell lines were treated with various plant extracts at different concentrations. MTT assays were performed to identify the most potent anti-tumor plant extract. Colony-formation assays were performed to determine the radiosensitization effect. To investigate the effect on migration, transwell migration assays were performed. Annexin V staining was performed to analyze cell apoptosis. 6-gingerol resulted in the most significant dose-dependent inhibition in all cell lines compared to other plant extracts. Colony-formation assays showed a significant radiosensitizing effect when 6-gingerol was combined with radiation. In addition, the combination of 6-gingerol with radiation resulted in a significant decrease in HNSCC cell migration. Mechanistically, Annexin V staining showed that the combination of 6-gingerol and RT induces a synergistic apoptotic effect in MOC1, MOC2 and SCC9 cells compared to RT alone. In conclusion, 6-gingerol enhances the effect of radiation in HNSCC cell lines and could be a suitable candidate for combination therapy in HNSCC.
Keywords: 6-gingerol; Apoptosis; Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma; Radiation.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Zerumbone acts as a radiosensitizer in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.Invest New Drugs. 2022 Apr;40(2):224-231. doi: 10.1007/s10637-021-01190-7. Epub 2021 Oct 6. Invest New Drugs. 2022. PMID: 34613571 Free PMC article.
-
Study on the sensitizing effect of SM-1 combined with irradiation on head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.Int J Radiat Biol. 2024;100(10):1453-1461. doi: 10.1080/09553002.2024.2381490. Epub 2024 Aug 13. Int J Radiat Biol. 2024. PMID: 39136543
-
The radiosensitizing effect of β-Thujaplicin, a tropolone derivative inducing S-phase cell cycle arrest, in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma-derived cell lines.Invest New Drugs. 2022 Aug;40(4):700-708. doi: 10.1007/s10637-022-01229-3. Epub 2022 Apr 12. Invest New Drugs. 2022. PMID: 35412173 Free PMC article.
-
Cell Death Induced by the Combination of Ephedra sinica Extract and Radiation in HNSCC is Positively Related to BAX and p-MLKL Expression.Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2024;24(1):50-57. doi: 10.2174/0118715206267182231024105837. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 37921146
-
Evidence-based radiation oncology in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.Radiother Oncol. 2007 Oct;85(1):156-70. doi: 10.1016/j.radonc.2007.04.002. Epub 2007 May 4. Radiother Oncol. 2007. PMID: 17482300 Review.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
