Evaluation of Neuromuscular Blockade: A Comparative Study of TOF-Cuff® on the Lower Leg and TOF-Scan® on the Ulnar Nerve During Mivacurium Anesthesia
- PMID: 39397356
- PMCID: PMC11488455
- DOI: 10.12659/MSM.945227
Evaluation of Neuromuscular Blockade: A Comparative Study of TOF-Cuff® on the Lower Leg and TOF-Scan® on the Ulnar Nerve During Mivacurium Anesthesia
Abstract
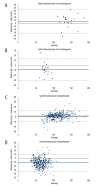
BACKGROUND To evaluate neuromuscular monitoring during anesthesia with mivacurium, this study assessed the correlation between measurements of TOF-Cuff® placed on the lower leg and stimulating the tibial nerve and TOF-Scan® values from the adductor pollicis muscle. Additionally, systolic (SBP) and diastolic (DBO) blood pressure measured in both locations were compared. MATERIAL AND METHODS Twenty-six patients participated in this observational clinical trial. The TOF-Cuff® was placed on the lower leg and the TOF-Scan® was placed on the thumb. Train-of-four (TOF) values were recorded simultaneously by both devices at 30-second intervals before intubation. Measurements continued every 5 minutes until extubation. Bland-Altman analyses compared TOF values obtained from the 2 devices. RESULTS Time to onset and relaxation time did not differ significantly; the number of patients presenting a lack of blockade despite TOF=0 was also concordant. The time from the last dose of mivacurium to TOF ratio >90 was shorter on the leg than on hand (median 20 [5-28, 0-65] min vs 30 [20-35, 0-60] min, p=0.025). The median (range, interquartile range) difference between measurements was: 11.6 (-41 to 45, 2-19) for SBP and -8 (-28 to 26, -15 to -4) for DBP at baseline (p=0.0495); 5 (-53 to 55, -2 to 9) for SBP and -11 (-45 to 29, -19 to -5) (p=0.0017) for DBP during the blockade. CONCLUSIONS Time-to-onset and SBP are comparable between these 2 methods, in contrast to time-to-recovery and diastolic blood pressure, and this should be considered in case of the inability to apply the TOF-Cuff on the leg.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



References
-
- Markle A, Graf N, Horn K, et al. Neuromuscular monitoring using TOF-Cuff® versus TOF-Scan®: An observational study under clinical anesthesia conditions. Minerva Anestesiol. 2020;86(7):704–11. - PubMed
-
- Iwasaki H, Nemes R, Brull SJ, et al. Quantitative neuromuscular monitoring: Current devices, new technological advances, and use in clinical practice. Curr Anesthesiol Rep. 2018;8:134–44.
-
- Murphy GS. Neuromuscular monitoring in the perioperative period. Anesth Analg. 2018;126(2):464–68. - PubMed
-
- Markle A, Graf N, Horn K, et al. Neuromuscular monitoring using TOF-Cuff® versus TOF-Scan®: An observational study under clinical anesthesia conditions. Minerva Anestesiol. 2020;86(7):704–11. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

