Efficacy and safety of immunotherapy combined with chemotherapy in patients with ES-SCLC: A systematic review and network meta-analysis of RCTs and RWSs
- PMID: 39397360
- PMCID: PMC11586137
- DOI: 10.1111/1759-7714.15458
Efficacy and safety of immunotherapy combined with chemotherapy in patients with ES-SCLC: A systematic review and network meta-analysis of RCTs and RWSs
Abstract
Objectives: To evaluate the efficacy and safety of programmed cell death 1 (PD-1)/programmed cell death ligand 1 (PD-L1) inhibitors in the treatment of extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer (ES-SCLC), we conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis that included randomized controlled trials (RCTs) and real-world studies (RWS).
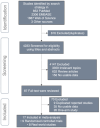
Methods: By scanning PubMed, Web of science, Embase, and other relevant clinical information public databases, nine RCTs and eight RWSs involving 5205 patients were included in the study. We directly compared the differences between chemotherapy and PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors plus chemotherapy, and determined the optimal treatment strategy through network meta-analysis (NMA).
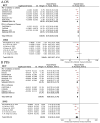
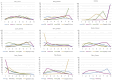
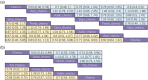
Results: Compared to chemotherapy, the addition of PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors significantly improves the overall survival (OS), progression-free survival (PFS), and objective response rate (ORR) in SCLC patients. Regarding safety, both RCTs and RWSs indicated no significant difference in grade 3-4 adverse events between chemotherapy and chemoimmunotherapy. NMA showed serplulimab plus chemotherapy (Serp_Chemo) appears to provide the best OS, PFS, and ORR benefit, while nivolumab plus chemotherapy shows higher toxicity than other regimens. In subgroup analysis, for elderly patients (age ≥65) and non-elderly (age <65) patients, the most promising quality regimens for achieving better OS extension are atezolizumab plus chemotherapy (Atez_Chemo) and Serp_Chemo, respectively. For patients with PD-L1 ≥ 1% and lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) > upper limit of normal (ULN), there is no apparent OS benefit from immune therapy.
Conclusions: In ES-SCLC treatment, adding PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors to standard chemotherapy improves OS, PFS, and ORR, with Serp_Chemo shows the most promise. Atez_Chemo and Serp_Chemo provided better survival for elderly and non-elderly patients, respectively.
Keywords: elderly; extensive stage small cell lung cancer; immune checkpoint inhibitors; meta‐analysis.
© 2024 The Author(s). Thoracic Cancer published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Cheng Y, Han L, Wu L, et al. LBA9 updated results of first‐line serplulimab versus placebo combined with chemotherapy in extensive‐stage small cell lung cancer: an international multicentre phase III study (ASTRUM‐005). Journal Article; Conference Proceeding. Ann Oncol. 2022;33:S1562. 10.1016/j.annonc.2022.10.351 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

