Changes in the frequency and amount of alcohol intake before and during the COVID-19 pandemic
- PMID: 39397380
- PMCID: PMC11561262
- DOI: 10.1093/joccuh/uiae055
Changes in the frequency and amount of alcohol intake before and during the COVID-19 pandemic
Abstract
Objectives: Concerns have been raised regarding the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on alcohol consumption patterns, which can have implications for public health. In this descriptive study, we aimed to show the change in the frequency and amount of alcohol consumption in Japan before and during the COVID-19 pandemic periods.
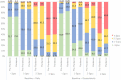
Methods: We analyzed data from annual health checkups among Japanese workers from April 2018 to March 2021. Changes in the frequency (daily, occasionally, rarely/never) and amount per one-time (4 categories by Japanese alcohol unit) of alcohol consumed among 331 200 participants were summarized by sex as 1-year changes in the periods before (fiscal year [FY] 2018 to FY 2019) and during (FY 2019 to FY 2020) the COVID-19 pandemic.
Results: Among daily drinkers and rarely/never drinkers, overall, 1-year changes in the frequency of alcohol consumption during the pandemic were mostly consistent with changes before the pandemic, for both sexes. The number of occasional drinkers who drank less frequently a year later increased during the pandemic compared with before the pandemic (from 9.6% to 11.6% among men and from 12.9% to 16.5% among women); however, occasional drinkers who drank more frequently showed a small increase. Collectively, both men and women showed a slight decrease in both the frequency and amount of alcohol consumption during the pandemic among occasional drinkers.
Conclusions: No major shifts in alcohol consumption habits occurred during the pandemic in our study population. Occasional drinkers tended to drink less during the pandemic, suggesting that initial concerns about increased alcohol consumption owing to the pandemic were unfounded.
Keywords: COVID-19; Japan; alcohol; alcohol consumption; consumption patterns; pandemic.
© The Author(s) [2024]. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Journal of Occupational Health.
Figures


References
-
- World Health Organization . Alcohol use and COVID-19. Published August 31, 2020. Accessed April 12, 2023. https://www.who.int/europe/emergencies/situations/covid-19/alcohol-use-a...
-
- Japan Medical Association . Covid-19 and alcoholism [in Japanese]. 2022. Accessed April 12, 2023. https://www.med.or.jp/dl-med/people/plaza/555.pdf
-
- World Health Organization . The impact of COVID-19 on global health goals. Published May 20, 2021. Accessed April 12, 2023. https://www.who.int/news-room/spotlight/the-impact-of-covid-19-on-global...
-
- Sugiyama S. Japan state of emergency to cover Tokyo, Osaka and five other prefectures. The Japan Times. Published April 6, 2020. Accessed April 12, 2023. https://www.japantimes.co.jp/news/2020/04/06/national/japan-state-of-eme...
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

