Opioid-induced Esophageal Dysfunction Masquerading as Type I Achalasia
- PMID: 39397629
- PMCID: PMC11474562
- DOI: 10.5056/jnm24088
Opioid-induced Esophageal Dysfunction Masquerading as Type I Achalasia
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
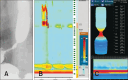
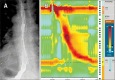
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

