A novel orf virus vector-based COVID-19 booster vaccine shows cross-neutralizing activity in the absence of anti-vector neutralizing immunity
- PMID: 39397784
- PMCID: PMC11485980
- DOI: 10.1080/21645515.2024.2410574
A novel orf virus vector-based COVID-19 booster vaccine shows cross-neutralizing activity in the absence of anti-vector neutralizing immunity
Abstract
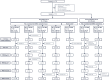
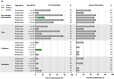
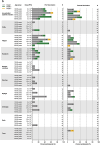
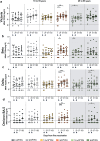
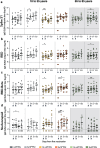
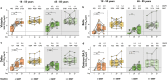
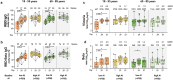
Next-generation COVID-19 vaccines are being developed to expand the breadth of coverage against existing and future variants and to extend the duration of protection. Prime-2-CoV_Beta is an orf virus (ORFV) based multi-antigen COVID-19 vaccine that co-expresses Spike (S) and Nucleocapsid (N) antigens. The safety and immunogenicity of Prime-2-CoV_Beta is investigated in a phase 1 first-in-human (FIH) dose-finding trial (ORFEUS study, ClinicalTrials.gov: NCT05367843). Participants of two age groups (18-55 and 65-85 years) who previously completed at least two doses of mRNA vaccines were enrolled and sequentially assigned to different dose groups to receive one intramuscular dose of 3 × 105, 3 × 106, 1.5 × 107, or 3 × 107 plaque-forming units (PFU) of Prime-2-CoV_Beta on day 1 and a second dose on day 29. Here, we report safety and immunogenicity data collected up to 6 months after the first study vaccination. Prime-2-CoV_Beta is safe and well tolerated and elicits immune responses at higher dose levels in participants aged 18-55. A single dose of 3 × 107 PFU boosted binding and cross-neutralizing antibody responses that are maintained through 6 months after the first booster vaccination. Polyfunctional S-specific CD4+ and CD8+ T cell responses are observed after vaccination. No pre-existing or vaccine-induced neutralizing anti-vector antibodies are detected. Our findings highlight the potential of the ORFV vector as a safe platform for future vaccine design, which provides the ability to deliver multiple antigens and allows for repeat immunization.
Keywords: COVID-19; ORF virus-vector; SARS-CoV-2 variants; booster vaccine; first-in-human trial; immunogenicity; safety.
Conflict of interest statement
Rald Amann holds ownership interest in Prime Vector Technologies GmbH, a company involved in the development of ORFV-based vaccines. Additionally, Ralf Amann is an inventor of patents related to ORFV, including a patent application of Prime-2-CoV. Ute Klinkhardt, Sylvia E. Schwarz and Madiha Derouazi were employed by Speransa Therapeutics GmbH. Arnaud M. Didierlaurent declared personal consulting fees for participation to scientific advisory boards for Speransa, Bioaster and Sanofi Pasteur, and participation on a Data Safety Monitoring Board for AMC Biosciences, all unrelated to the present work and is the chairman of the WHO Technical advisory group for Emergency use listing of COVID-19 vaccines..
Figures

References
-
- Ahn JY, Lee J, Suh YS, Song YG, Choi YJ, Lee KH, Seo SH, Song M, Oh J-W, Kim M, et al. Safety and immunogenicity of two recombinant DNA COVID-19 vaccines containing the coding regions of the spike or spike and nucleocapsid proteins: an interim analysis of two open-label, non-randomised, phase 1 trials in healthy adults. Lancet Microbe. 2022;3(3):173–183. doi:10.1016/S2666-5247(21)00358-X. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
