Early heart disease prediction using feature engineering and machine learning algorithms
- PMID: 39397946
- PMCID: PMC11471268
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e38731
Early heart disease prediction using feature engineering and machine learning algorithms
Abstract
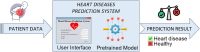
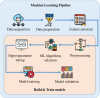
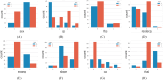
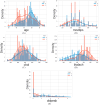
Heart disease is one of the most widespread global health issues, it is the reason behind around 32 % of deaths worldwide every year. The early prediction and diagnosis of heart diseases are critical for effective treatment and sickness management. Despite the efforts of healthcare professionals, cardiovascular surgeons and cardiologists' misdiagnosis and misinterpretation of test results may happen every day. This study addresses the growing global health challenge raised by Cardiovascular Diseases (CVDs), which account for 32 % of all deaths worldwide, according to the World Health Organization (WHO). With the progress of Machine Learning (ML) and Deep Learning (DL) techniques as part of Artificial Intelligence (AI), these technologies have become crucial for predicting and diagnosing CVDs. This research aims to develop an ML system for the early prediction of cardiovascular diseases by choosing one of the powerful existing ML algorithms after a deep comparative analysis of several. To achieve this work, the Cleveland and Statlog heart datasets from international platforms are used in this study to evaluate and validate the system's performance. The Cleveland dataset is categorized and used to train various ML algorithms, including decision tree, random forest, support vector machine, logistic regression, adaptive boosting, and K-nearest neighbors. The performance of each algorithm is assessed based on accuracy, precision, recall, F1 score, and the Area Under the Curve metrics. Hyperparameter tuning approaches have been employed to find the best hyperparameters that reflect the optimal performance of the used algorithms based on different evaluation approaches including 10-fold cross-validation with a 95 % confidence interval. The study's findings highlight the potential of ML in improving the early prediction and diagnosis of cardiovascular diseases. By comparing and analyzing the performance of the applied algorithms on both the Cleveland and Statlog heart datasets, this research contributes to the advancement of ML techniques in the medical field. The developed ML system offers a valuable tool for healthcare professionals in the early prediction and diagnosis of cardiovascular diseases, with implications for the prediction and diagnosis of other diseases as well.
Keywords: Artificial intelligence; Cardiovascular diseases; Classification; Deep learning; Machine learning; Prediction.
© 2024 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures





References
-
- Denysyuk H.V., Pinto R.J., Silva P.M., Duarte R.P., Marinho F.A., Pimenta L., Gouveia A.J., Gonçalves N.J., Coelho P.J., Zdravevski E., Lameski P., Leithardt V., Garcia N.M., Pires I.M. Algorithms for automated diagnosis of cardiovascular diseases based on ECG data: a comprehensive systematic review. Heliyon. 2023;9 doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e13601. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Collins C., Dennehy D., Conboy K., Mikalef P. Artificial intelligence in information systems research: a systematic literature review and research agenda. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2021;60 doi: 10.1016/j.ijinfomgt.2021.102383. - DOI
-
- Shinde P.P., Shah S. 2018 Fourth Int. Conf. Comput. Commun. Control Autom. ICCUBEA. 2018. A review of machine learning and deep learning applications; pp. 1–6. - DOI
-
- Zhang S., Zhou H., Zhang L. Recent machine learning progress in image analysis and understanding. Adv. Multimed. 2018;2018:1–2. doi: 10.1155/2018/1685890. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

