Psychological problems and their impact on oral mucosal disease patients' quality of life: A cross-sectional study in the Chinese population
- PMID: 39397995
- PMCID: PMC11471221
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e38210
Psychological problems and their impact on oral mucosal disease patients' quality of life: A cross-sectional study in the Chinese population
Abstract
Objectives: We aimed to investigate the presence of common psychological factors (i.e., stress, depression, anxiety) and their impact on the Oral health-related quality of life (OHRQoL) in patients diagnosed with four oral mucosal diseases (OMDs): recurrent aphthous ulcers (RAU), oral lichen planus (OLP), oral leukoplakia (OLK), and oral submucous fibrosis (OSF).
Methods: A total of 229 patients with clinically diagnosed OMDs were enrolled in this study, consisting of 55 RAU, 68 OLK, 50 OLP, and 56 OSF patients. The patients were statistically analyzed for psychological problems and OHRQoL using the Visual Analog Scale (VAS)、 the 5-item Oral Health Impact Profile (OHIP-5) and the Depression Anxiety Stress Scale-21 (DASS-21) scales.
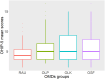
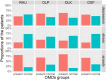
Results: There were 229 valid questionnaires collected, consisting of 83 females and 146 males with a mean age of 45.24 (SD = 11.88) years. Multiple regressions between DASS-21 scores and OHIP-5 scores revealed generally negative impacts of psychological problems on OHRQoL, with depression on OLP (β = 0.47), OLK (β = 0.65) and OSF (β = 0.38), stress on RAU (β = 0.29), OLP (β = 0.72), OLK (β = 0.38) and OSF (β = 0.60), and anxiety on OLP (β = 0.33), OLK (β = 0.49) and OSF (β = 0.51).
Conclusions: Psychological problems like depression, stress, and anxiety were found to be prevalent in OMDs patients and adversely affected their OHRQoL. The results support the biopsychosocial medical model in the treatment of OMDs patients.
Clinical significance: The present study reinforced the crucial roles of psychological factors in impacting OMDs patients' OHRQoL. Therefore, it is necessary to monitor patients' psychological status and OHRQoL using questionnaires like DASS-21 and OHIP-5. Followed by psychological interventions, the treatment is expected to be enhanced.
Keywords: DASS-21; OHIP-5; Oral health-related quality of life; Oral mucosal; Psychometrics.
© 2024 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
References
-
- Specialized Committee on Oral Mucosal Diseases of the Chinese Stomatological Association(CMA) Chinese Stomatological Association of Chinese and Western Medicine Combined Specialized Committee. Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of oral lichen planus (revised edition) J Chinese Journal of Stomatology. 2022;57(2):115–121. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112144-20211115-00505. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

