Comparative study on the bioavailability of peptide extracts from Jeju black pigs and three-way crossbred pigs
- PMID: 39398300
- PMCID: PMC11466743
- DOI: 10.5187/jast.2023.e86
Comparative study on the bioavailability of peptide extracts from Jeju black pigs and three-way crossbred pigs
Abstract
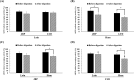
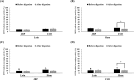
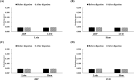
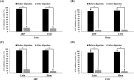
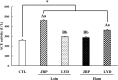
This study aimed to compare the changes in the bioactivities of peptide extracts (< 10 kDa) obtained from Jeju black pigs (JBP) and three-way crossbred pigs (Landrace × Yorkshire × Duroc, LYD) before and after digestion. The results showed that the loin peptide extracts of JBP maintained high 2,2'-azino-bis (3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulfonic acid) (ABTS) radical scavenging activity after in vitro digestion. However, the iron chelating activity and antihypertensive activity of all peptide extracts were decreased. This study suggested that the peptide extracts produced through alkaline-AK digestion have sufficiently high antioxidant and antihypertensive activities; however, these activities were reduced after in vitro digestion. Meanwhile, the JBP loin and ham peptide extracts promoted high superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity than that of LYD when administered to mice. Furthermore, the ham peptide extracts of JBP showed a relatively high antihypertensive activity in mice. Therefore, it is deemed that these peptide extracts from JBP are more bioactive than that of LYD, and can be used as bioactive materials.
Keywords: Antihypertensive activity; Antioxidant activity; Jeju black pigs; Peptide extracts.
© Copyright 2024 Korean Society of Animal Science and Technology.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures


References
-
- Jin SK, Kim CW, Song YM, Jang WH, Kim YB, Yeo JS, et al. Physicochemical characteristics of longissimus muscle between the Korean native pig and Landrace. Korean J Food Sci Anim Resour. 2001;21:142–8.
-
- Kim GW, Kim HY, Chun JY. Different characteristics between improved breeds and Jeju black pigs; 2016 KFN International Symposium and Annual Meeting; Jeju, Korea. 2016. pp. 320–1. In. p.
-
- Arihara K. Functional properties of bioactive peptides derived from meat proteins. In: Nollet LML, Toldrá F, editors. Advanced technologies for meat processing. Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press; 2006. pp. 245–74. p. - DOI
-
- Sánchez A, Vázquez A. Bioactive peptides: a review. Food Qual Saf. 2017;1:29–46. doi: 10.1093/fqsafe/fyx006. - DOI
-
- Katayama K, Mori T, Kawahara S, Miake K, Kodama Y, Sugiyama M, et al. Angiotensin-I converting enzyme inhibitory peptide derived from porcine skeletal muscle myosin and its antihypertensive activity in spontaneously hypertensive rats. J Food Sci. 2007;72:S702–6. doi: 10.1111/j.1750-3841.2007.00571.x. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

