A systematic scoping review of the multifaceted role of phoenixin in metabolism: insights from in vitro and in vivo studies
- PMID: 39398330
- PMCID: PMC11466790
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1406531
A systematic scoping review of the multifaceted role of phoenixin in metabolism: insights from in vitro and in vivo studies
Abstract
Phoenixin (PNX) is an emerging neuropeptide that plays a significant role in regulating metabolism and reproduction. This comprehensive review examines findings from human, in vivo, and in vitro studies to elucidate the functions of PNX in metabolic processes. PNX has been identified as a key player in essential metabolic pathways, including energy homeostasis, glucose, lipid and electrolyte metabolism, and mitochondrial dynamics. It modulates food and fluid intake, influences glucose and lipid profiles, and affects mitochondrial biogenesis and function. PNX is abundantly expressed in the hypothalamus, where it plays a crucial role in regulating reproductive hormone secretion and maintaining energy balance. Furthermore, PNX is also expressed in peripheral tissues such as the heart, spleen, and pancreas, indicating its involvement in the regulation of metabolism across central and peripheral systems. PNX is a therapeutic peptide that operates through the G protein-coupled receptor 173 (GPR173) at the molecular level. It activates signaling pathways such as cAMP-protein kinase A (PKA) and Epac-ERK, which are crucial for metabolic regulation. Research suggests that PNX may be effective in managing metabolic disorders like obesity and type 2 diabetes, as well as reproductive health issues like infertility. Since metabolic processes are closely linked to reproduction, further understanding of PNX's role in these areas is necessary to develop effective management/treatments. This review aims to highlight PNX's involvement in metabolism and identify gaps in current knowledge regarding its impact on human health. Understanding the mechanisms of PNX's action is crucial for the development of novel therapeutic strategies for the treatment of metabolic disorders and reproductive health issues, which are significant public health concerns globally.
Keywords: glycolysis; metabolism; mitochondria; mitochondrial respiration; phoenixin (PNX).
Copyright © 2024 Muzammil, Barathan, Yazid, Sulaiman, Makpol, Mohamed Ibrahim, Jaafar and Abdullah.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision
Figures

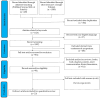
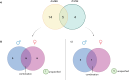

References
-
- Hermanowicz B, Bogus-Nowakowska K, Palasz A, Wiaderkiewicz R, Robak A. Phoenixin is present in hypothalamic neuroendocrine nuclei of the domestic pig-immunohistochemical study. Acta Neurobiologiae Experimentalis. (2015) 75).
-
- Kras K, Ropka-Molik K, Muszyński S, Arciszewski MB. Expression of Genes Encoding Selected Orexigenic and Anorexigenic Peptides and Their Receptors in the Organs of the Gastrointestinal Tract of Calves and Adult Domestic Cattle (Bos taurus taurus). Int J Mol Sci. (2023) 25:533. doi: 10.3390/ijms25010533 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

