Relationship of Corneal Biomechanics Measured by Corvis ST and Optic Nerve Head Parameters in Healthy Saudi Females
- PMID: 39398470
- PMCID: PMC11471078
- DOI: 10.2147/OPTH.S469150
Relationship of Corneal Biomechanics Measured by Corvis ST and Optic Nerve Head Parameters in Healthy Saudi Females
Abstract
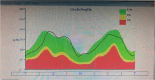
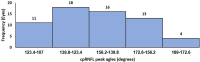
Aim: This study assessed the correlation between corneal biomechanical properties measured with Corvis ST (CST) and retinal nerve fiber layer thickness profile, anterior lamina cribrosa surface depth, and other optic nerve head parameters in healthy Saudi females.
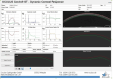
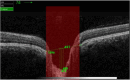
Methods: This study included 62 eyes (only right eyes) of 62 healthy Saudi females aged from 20 to 39 yrs. A complete ophthalmologic assessment was performed for all participants. In addition, corneal biomechanical parameters were measured using CST, and optic nerve head parameters were evaluated using spectral domain optical coherence tomography.
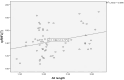
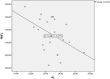
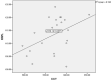
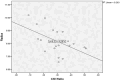
Results: This study demonstrated a significant weak positive correlation between circumpapillary retinal nerve fiber layer (cpRNFL) peak angle and only second applanation (A2) length (mm) (r = 0.293, P = 0.021). Also, this study reported a significant moderate negative association between the C/D ratio and radius (r = -.513, P = 0.015). However, there was no significant correlation between corneal biomechanics and ALCSD in this study.
Conclusion: This study reported a significant positive correlation between cpRNFL peak angle and A2-length. In addition, the current study documented a significant moderate negative association between C/D ratio and radius. However, there was no significant correlation between ALCSD and the corneal biomechanical properties in this study. Further research is needed to verify the impact of corneal biomechanics on optic nerve head parameters and further investigate its role in the pathophysiology of glaucoma.
Keywords: anterior lamina cribrosa surface depth; circumpapillary retinal nerve fiber layer peak angle; corneal biomechanics.
© 2024 Elagamy et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

