The dose-effect response of combined red and infrared photobiomodulation on insulin resistance in skeletal muscle cells
- PMID: 39398538
- PMCID: PMC11470420
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbrep.2024.101831
The dose-effect response of combined red and infrared photobiomodulation on insulin resistance in skeletal muscle cells
Abstract
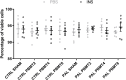
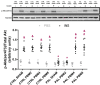
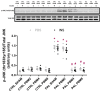
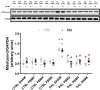
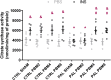
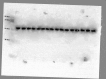
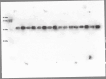
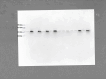
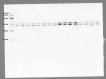
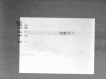
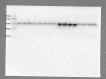
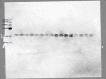
Obesity is a major public health problem and is a major contributor to the development of insulin resistance. In previous studies we observed that single-wavelength red or infrared photobiomodulation (PBM) improved insulin signaling in adipocytes and skeletal muscle of mice fed a high-fat diet, but information about the combination of different wavelengths, as well as the effect of different light doses (J/cm2) is lacking. Therefore, the aim of this study was to investigate the effects of different doses of dual-wavelength PBM on insulin signaling in muscle cell, and explore potential mechanisms involved. Mouse myoblasts (C2C12) were differentiated into myotubes and cultured in palmitic acid, sodium oleate and l-carnitine (PAL) to induce insulin resistance high or in glucose medium (CTRL). Then, they received SHAM treatment (lights off, 0 J/cm2) or PBM (660 + 850 nm; 2, 4 or 8 J/cm2). PAL induced insulin resistance (assessed by Akt phosphorylation at ser473), attenuated maximal citrate synthase activity, and increased the phosphorylation of c-Jun NH(2) terminal kinase (JNK) (T183/Y185). PBM at doses of 4 or 8 J/cm2 reversed these PAL-induced responses. Furthermore, at doses of 2, 4 or 8 J/cm2, PBM reversed the increase in mitofusin-2 content induced by PAL. In conclusion, the combination of dual-wavelength red and infrared PBM at doses of 4 and 8 J/cm2 improved intracellular insulin signaling in musculoskeletal cells, and this effect appears to involve the modulation of mitochondrial function and the attenuation of the activation of stress kinases.
Keywords: C2C12 cells; Inflammation; Light-emitting diode; Lipotoxicity; Mitochondrial dysfunction; Muscle tissue; Obesity; Photobiomodulation therapy; Type 2 diabetes.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures







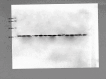




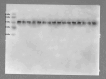
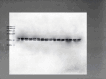





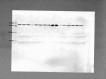







References
-
- World Health Organization (WHO) Obesity and overweight. 2024. https://www.Who.Int/News-Room/Fact-Sheets/Detail/Obesity-and-Overweight
-
- WHO - WORLD HEALTH ORGANIZATION Obesity. 2021 https://www.Who.Int/News-Room/Facts-in-Pictures/Detail/6-Facts-on-Obesit...
-
- J.H.U.& M. (JHU) JHU COVID-19 dashboard by the center for systems science and engineering (CSSE) at johns hopkins university (JHU) 2023. https://Coronavirus.Jhu.Edu/Map.Html
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

