Cytotoxicity induced by three commercial neonicotinoid insecticide formulations in differentiated human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells
- PMID: 39399211
- PMCID: PMC11464667
- DOI: 10.1093/toxres/tfae171
Cytotoxicity induced by three commercial neonicotinoid insecticide formulations in differentiated human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells
Abstract
Background: Neonicotinoid insecticides are used worldwide for crop protection. They act as agonists at postsynaptic nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (nAChRs), disrupting normal neurotransmission in target insects. Human exposure is high due to the widespread use of neonicotinoids and their residues in food. This study aimed to evaluate the in vitro neurotoxicity of three neonicotinoid commercial formulations Much 600 FS® (imidacloprid 600 g L-1), Evidence 700 WG® (imidacloprid 700 g kg-1), and Actara 250 WG® (thiamethoxam 250 g kg-1) in differentiated human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cell line.
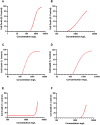
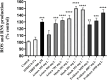
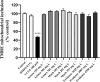
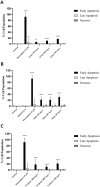
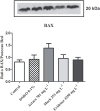
Methods: Cells were incubated with the pesticides for 96 h, and the cytotoxicity was evaluated through the 3-(4,5-dimethyl-2-thiazolyl)-2,5-diphenyl-2H-tetrazolium·bromide (MTT) reduction and neutral red (NR) uptake assays. Toxicological pathways such as reactive oxygen (ROS) and nitrogen species (RNS) production, mitochondrial membrane potential, cell death mode, and the expression of the pro-apoptotic protein Bax were also evaluated.
Results: EC50 values of 266.4, 4,175, and 653.2 mg L-1 were found for Much®, Evidence® and Actara®, respectively. Significant increases in ROS and RNS generation were observed for all pesticides, while mitochondrial membrane potential and Bax protein expression showed no significant changes. Analysis of cell death mode revealed an increase in early apoptotic cells.
Conclusion: Therefore, neonicotinoid insecticides are potentially neurotoxic, reinforcing concerns about human exposure to these commercial formulations.
Keywords: apoptosis; cytotoxicity; imidacloprid; neonicotinoids; reactive species production; thiamethoxam.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press. All rights reserved. For Permissions, please email: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures
References
-
- Jeschke P, Nauen R, Schindler M, Elbert A. Overview of the status and global strategy for neonicotinoids. J Agric Food Chem. 2011:59(7):2897–2908. - PubMed
-
- Goulson D. An overview of the environmental risks posed by neonicotinoid insecticides. J Appl Ecol. 2013:50(4):977–987.
-
- Han W, Tian Y, Shen X. Human exposure to neonicotinoid insecticides and the evaluation of their potential toxicity: an overview. Chemosphere. 2018:192:59–65. - PubMed
-
- Liao L, Sun T, Gao Z, Lin J, Gao M, Li A, Gao T, Gao Z. Neonicotinoids as emerging contaminants in China’s environment: a review of current data. Environ Sci Pollut Res. 2024:31(39):51098–51113. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

