Risk of Skull Perforation with Halo Vest Skull Pins
- PMID: 39399451
- PMCID: PMC11464829
- DOI: 10.22603/ssrr.2023-0261
Risk of Skull Perforation with Halo Vest Skull Pins
Abstract
Introduction: A halo vest is an immobilization device widely used to stabilize the cervical spine. Pain and infection at the skull pin insertion site are common complications, but skull perforation is rare, and most published studies are case reports. This study aimed to identify risk factors for skull perforation by comparing patients who did and did not develop perforation.
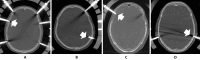
Methods: Overall thickness and the thicknesses of the internal and external laminae of the skull at the skull pin insertion sites were measured on cranial computed tomography scans of 66 patients fitted with a halo vest. The results were compared between patients who did and did not develop perforation.
Results: Four patients developed perforations. All patients with perforation were older women, and their external and internal laminae were significantly thinner than those of patients who did not develop perforation.
Conclusions: The reported causes of skull pin perforation include infection around the pin, osteoporosis, and an enlarged frontal sinus. However, most patients with perforation in the present study were older women, and the cause was the thinning of the external and external laminae.
Keywords: Halo vest; Osteoporosis; Skull perforation; Skull pin.
Copyright © 2024 The Japanese Society for Spine Surgery and Related Research.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: The authors declare that there are no relevant conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Garfin SR, Botte MJ, Waters RL, et al. Complications in the use of the halo fixation device. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1986;68(3):320-5. - PubMed
-
- van Middendorp JJ, Slooff WB, Nellestein WR, et al. Incidence of and risk factors for complications associated with halo-vest immobilization: a prospective, descriptive cohort study of 239 patients. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2009;91(1):71-9. - PubMed
-
- Saeed MU, Dacuycuy MAC, Kennedy DJ. Halo pin insertion-associated brain abscess: case report and review of literature. Spine. 2007;32(8):E271-4. - PubMed
-
- Hioki A, Miyamoto K, Inoue T, et al. Successful antibiotic treatment for subdural empyema and seizure due to methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus as a complication of halo orthosis usage: a case report. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2012;22:25-8. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
