Association of the oxidative balance score and chronic kidney disease: insights from the national health and nutrition examination survey 2009-2018
- PMID: 39399530
- PMCID: PMC11468420
- DOI: 10.3389/fnut.2024.1429191
Association of the oxidative balance score and chronic kidney disease: insights from the national health and nutrition examination survey 2009-2018
Abstract
Introduction: Oxidative stress plays a pivotal role in the pathogenesis of chronic kidney disease (CKD). The oxidative balance score (OBS) was devised to quantify the overall oxidative state, integrating pro-oxidant and antioxidant influences from both dietary intake and lifestyle practices. The aim of this study was to delve into the relationship between the OBS and CKD within the adult population of the United States.
Methods: Utilizing data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) spanning 2009-2018, we derived the OBS from 16 dietary and four lifestyle factors. We employed weighted multivariate regression to probe the link between OBS and CKD. Additionally, we undertook subgroup analyses and applied Restricted Cubic Spline Regression (RCS) for further data analyses.
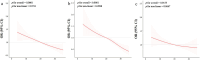
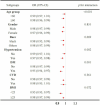
Results: This study encompassed 19,444 participants. Logistic regression analysis consistently demonstrated a protective effect of higher OBS on CKD. In Model 3, each unit increase in OBS was associated with a 2% reduction in the risk of CKD (95% CI: 0.97-0.99, p < 0.001) and a 4% reduction in the risk of reduced estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) (95% CI: 0.95-0.98, p < 0.001). The highest OBS quintile (Q4) also showed significant reductions in the risk of CKD (OR: 0.66, 95% CI: 0.53-0.82, p < 0.001) and reduced eGFR (OR: 0.51, 95% CI: 0.37-0.69, p < 0.001) in Model 3. RCS analysis revealed a linear relationship between OBS and CKD. Subgroup analyses indicated significant associations between OBS and CKD in most subgroups, except for those without hypertension or with cardiovascular disease. Additionally, interaction analyses demonstrated that age, hypertension, and diabetes significantly modify the association between OBS and CKD risk.
Conclusion: An elevated OBS, reflecting a predominance of antioxidants, correlates with a diminished CKD risk in the American adult demographic. These insights emphasize the potential influence of oxidative equilibrium on the development of CKD.
Keywords: NHANES; antioxidants; chronic kidney disease; cross-sectional study; oxidative balance score.
Copyright © 2024 Chen, Wu, Hou, Yu, Gao, Gou and Fu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Association between chronic kidney disease and oxidative balance score: National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) 2005-2018.Front Nutr. 2025 Jan 3;11:1406780. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2024.1406780. eCollection 2024. Front Nutr. 2025. PMID: 39830066 Free PMC article.
-
Association of oxidative balance score with chronic kidney disease: NHANES 1999-2018.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024 Jun 11;15:1396465. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1396465. eCollection 2024. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 38919480 Free PMC article.
-
Associations between oxidative balance score and chronic kidney disease events in US adults: a population-based study.Sci Rep. 2024 Jun 14;14(1):13743. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-64147-9. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38877058 Free PMC article.
-
Association between oxidative balance score in adults with and without chronic kidney disease: 2011-2028 NHANES.Front Nutr. 2024 Apr 23;11:1374719. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2024.1374719. eCollection 2024. Front Nutr. 2024. PMID: 38725577 Free PMC article.
-
Association between oxidative balance score and diabetic kidney disease, low estimated glomerular filtration rate and albuminuria in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients: a cross-sectional study.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024 Jul 31;15:1412823. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1412823. eCollection 2024. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 39145317 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The interaction between sleep patterns and oxidative balance scores on the risk of cognitive function decline: Results from the national health and nutrition examination survey 2011-2014.PLoS One. 2024 Dec 27;19(12):e0313784. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0313784. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39729482 Free PMC article.
-
Associations between oxidative balance score and chronic kidney disease events in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients: a cross‑sectional study.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 1;15(1):21215. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-05281-w. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40594388 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sies H. Hydroperoxides and thiol oxidants in the study of oxidative stress in intact cells and organs. Oxidative Stress. 1. Cambridge, MA: Academic Press, pp. 73–90. (1985).
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

