Advances in magnetic resonance imaging for the assessment of paediatric focal epilepsy: a narrative review
- PMID: 39399717
- PMCID: PMC11467228
- DOI: 10.21037/tp-24-166
Advances in magnetic resonance imaging for the assessment of paediatric focal epilepsy: a narrative review
Abstract
Background and objective: Epilepsy affects approximately 50 million people worldwide, with 30-40% of patients not responding to medication, necessitating alternative therapies such as surgical intervention. However, the accurate localization of epileptogenic lesions, particularly in pediatric magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)-negative drug-resistant epilepsy, remains a challenge. This paper reviews advanced neuroimaging techniques aimed at improving the detection of such lesions to enhance surgical outcomes.
Methods: A comprehensive literature search was conducted using PubMed, focusing on advanced MRI sequences, focal epilepsy, and the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) in the diagnostic process.
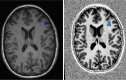
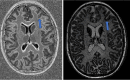
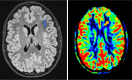
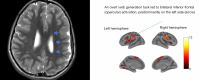
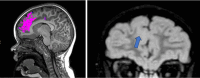
Key content and findings: New MRI sequences, including magnetization prepared 2 rapid gradient echo (MP2RAGE), edge-enhancing gradient echo (EDGE), and fluid and white matter suppression (FLAWS), have demonstrated enhanced capabilities in detecting subtle epileptogenic lesions. Quantitative MRI techniques, notably magnetic resonance fingerprinting (MRF), alongside innovative post-processing methods, are emphasized for their effectiveness in delineating cortical malformations, whether used alone or in combination with ultra-high field MRI systems. Furthermore, the integration of AI in radiology is progressing, providing significant support in accurately localizing lesions, and potentially optimizing pre-surgical planning.
Conclusions: While advanced neuroimaging and AI offer significant improvements in the diagnostic process for epilepsy, some challenges remain. These include long acquisition times, the need for extensive data analysis, and a lack of large, standardized datasets for AI validation. However, the future holds promise as research continues to integrate these technologies into clinical practice. These efforts will improve the clinical applicability and effectiveness of these advanced techniques in epilepsy management, paving the way for more accurate diagnoses and better patient outcomes.
Keywords: Focal epilepsy; artificial intelligence (AI); malformations of cortical development (MCDs); neuroimaging; paediatric.
2024 AME Publishing Company. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://tp.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/tp-24-166/coif). F.D.A. serves as an unpaid editorial board member of Translational Pediatrics from March 2024 to February 2026. The other authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Integrating standard epilepsy protocol, ASL-perfusion, MP2RAGE/EDGE and the MELD-FCD classifier in the detection of subtle epileptogenic lesions: a 3 Tesla MRI pilot study.Neuroradiology. 2025 Mar;67(3):665-675. doi: 10.1007/s00234-024-03488-8. Epub 2024 Oct 23. Neuroradiology. 2025. PMID: 39441414
-
MP2RAGE and Susceptibility-Weighted Imaging in Lesional Epilepsy at 7T.J Neuroimaging. 2018 Jul;28(4):365-369. doi: 10.1111/jon.12523. Epub 2018 May 24. J Neuroimaging. 2018. PMID: 29797439
-
Computational analysis in epilepsy neuroimaging: A survey of features and methods.Neuroimage Clin. 2016 Feb 23;11:515-529. doi: 10.1016/j.nicl.2016.02.013. eCollection 2016. Neuroimage Clin. 2016. PMID: 27114900 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gray-matter-specific MR imaging improves the detection of epileptogenic zones in focal cortical dysplasia: A new sequence called fluid and white matter suppression (FLAWS).Neuroimage Clin. 2018 Aug 11;20:388-397. doi: 10.1016/j.nicl.2018.08.010. eCollection 2018. Neuroimage Clin. 2018. PMID: 30128277 Free PMC article.
-
Malformations of cortical development: The role of 7-Tesla magnetic resonance imaging in diagnosis.Rev Neurol (Paris). 2019 Mar;175(3):157-162. doi: 10.1016/j.neurol.2019.01.393. Epub 2019 Mar 1. Rev Neurol (Paris). 2019. PMID: 30827579 Review.
References
-
- Epilepsy [Internet]. [cited 2024 Jan 14]. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/epilepsy
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
