Protective effects of pistachio hydroalcoholic extract on morphine-induced analgesic tolerance and dependence: investigating the impact of oxidative stress
- PMID: 39399729
- PMCID: PMC11468171
- DOI: 10.4103/RPS.RPS_85_22
Protective effects of pistachio hydroalcoholic extract on morphine-induced analgesic tolerance and dependence: investigating the impact of oxidative stress
Abstract
Background and purpose: Chronic consumption of morphine (Mor) induces tolerance and dependence. This study aimed to survey the effects of pistachio extract (PX) on the induction and expression of Mor analgesic tolerance and physical dependency in mice.
Experimental approach: Animals were randomly separated into six groups (n = 7): control, DMSO, Mor (10 mg/kg), Mor + saline, Mor + PX (10 mg/kg), and Mor + PX (100 mg/kg). Mor was injected (10 mg/kg, twice a day, s.c.) for 7 days to induce tolerance. PX was administered (10 and 100 mg/kg, orally) during the examination period. On each day and 20 min after Mor administration, a tail-flick test was done to measure the analgesic response and induction of tolerance. On day 7, naloxone (5 mg/kg, s.c.) was injected into the Mor-dependent animals to evaluate dependence, and animals were monitored for 30 min for jumping. Also, malondialdehyde (MDA), superoxide dismutase (SOD), and glutathione peroxidase (GPx) were assessed in the brain tissue.
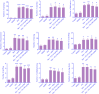
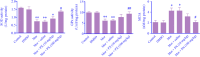
Findings/results: Our results indicated that co-administration of PX with Mor for 7 days diminished the induction of Mor tolerance. PX administration for 7 days alongside Mor reduced the frequency of withdrawal signs in naloxone-injected animals during dependence induction. Also, Mor increased the level of MDA and decreased the activities of SOD and GPx. Treatment with PX (100 mg/kg) restored all of the mentioned abnormalities.
Conclusion and implications: According to the results presented in this study, chronic administration of PX forbade the induction of Mor analgesic tolerance and dependency in mice.
Keywords: Mice; Morphine; Physical dependence; Pistachio extract; Tolerance.
Copyright: © 2024 Research in Pharmaceutical Sciences.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared no conflict of interest in this study.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Effects of valsartan on morphine tolerance and dependence in rats.Res Pharm Sci. 2021 May 12;16(3):286-293. doi: 10.4103/1735-5362.314827. eCollection 2021 Jun. Res Pharm Sci. 2021. PMID: 34221062 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of metformin on morphine analgesic tolerance and dependence in rats.Res Pharm Sci. 2018 Aug;13(4):316-323. doi: 10.4103/1735-5362.235158. Res Pharm Sci. 2018. PMID: 30065764 Free PMC article.
-
Antinociceptive effects of morphine and naloxone in mu-opioid receptor knockout mice transfected with the MORS196A gene.J Biomed Sci. 2010 Apr 20;17(1):28. doi: 10.1186/1423-0127-17-28. J Biomed Sci. 2010. PMID: 20403204 Free PMC article.
-
A therapeutic strategy to prevent morphine dependence and tolerance by coadministration of cAMP-related reagents with morphine.Methods Find Exp Clin Pharmacol. 1998 Sep;20(7):619-25. doi: 10.1358/mf.1998.20.7.485728. Methods Find Exp Clin Pharmacol. 1998. PMID: 9819808 Review.
-
The mechanism of μ-opioid receptor (MOR)-TRPV1 crosstalk in TRPV1 activation involves morphine anti-nociception, tolerance and dependence.Channels (Austin). 2015;9(5):235-43. doi: 10.1080/19336950.2015.1069450. Epub 2015 Jul 15. Channels (Austin). 2015. PMID: 26176938 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Somogyi AA, Barratt DT, Coller JK. Pharmacogenetics of opioids. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2007;81(3):429–444. DOI: 10.1038/sj.clpt.6100095. - PubMed
-
- Hemati K, Pourhanifeh MH, Dehdashtian E, Fatemi I, Mehrzadi S, Reiter RJ, et al. Melatonin and morphine: potential beneficial effects of co-use. Fundam Clin Pharmacol. 2021;35(1):25–39. DOI: 10.1111/fcp.12566. - PubMed
-
- Rezazadeh H, Hosseini Kahnouei M, Hassanshahi G, Allahtavakoli M, Shamsizadeh A, Roohbakhsh A, et al. Regulatory effects of chronic low-dose morphine on nitric oxide level along with baroreflex sensitivity in two-kidney one-clip hypertensive rats. Iran J Kidney Dis. 2014;8(3):194–200. PMID: 24878941. - PubMed
-
- Saffar S, Fatemi I, Rahmani M, Hassanshahi J, Sahamsizadeh A, Allahtavakoli M, et al. The effect of epigallocatechin-3-gallate on morphine-induced memory impairments in rat: EGCG effects on morphine neurotoxicity. Hum Exp Toxicol. 2020;39(7):994–1002. DOI: 10.1177/0960327120909540. - PubMed
-
- Mercadante S, Arcuri E, Santoni A. Opioid-induced tolerance and hyperalgesia. CNS Drugs. 2019;33(10):943–955. DOI: 10.1007/s40263-019-00660-0. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
