Identification of Pathogenic Copy Number Variants in Mexican Patients With Inherited Retinal Dystrophies Applying an Exome Sequencing Data-Based Read-Depth Approach
- PMID: 39400524
- PMCID: PMC11472028
- DOI: 10.1002/mgg3.70019
Identification of Pathogenic Copy Number Variants in Mexican Patients With Inherited Retinal Dystrophies Applying an Exome Sequencing Data-Based Read-Depth Approach
Abstract
Background: Retinal dystrophies (RDs) are the most common cause of inherited blindness worldwide and are caused by genetic defects in about 300 different genes. While targeted next-generation sequencing (NGS) has been demonstrated to be a reliable and efficient method to identify RD disease-causing variants, it doesn't routinely identify pathogenic structural variant as copy number variations (CNVs). Targeted NGS-based CNV detection has become a crucial step for RDs molecular diagnosis, particularly in cases without identified causative single nucleotide or Indels variants. Herein, we report the exome sequencing (ES) data-based read-depth bioinformatic analysis in a group of 30 unrelated Mexican RD patients with a negative or inconclusive genetic result after ES.
Methods: CNV detection was performed using ExomeDepth software, an R package designed to detect CNVs using exome data. Bioinformatic validation of identified CNVs was conducted through a commercially available CNV caller. All identified candidate pathogenic CNVs were orthogonally verified through quantitative PCR assays.
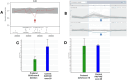
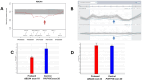
Results: Pathogenic or likely pathogenic CNVs were identified in 6 out of 30 cases (20%), and of them, a definitive molecular diagnosis was reached in 5 cases, for a final diagnostic rate of ~17%. CNV-carrying genes included CLN3 (2 cases), ABCA4 (novel deletion), EYS, and RPGRIP1.
Conclusions: Our results indicate that bioinformatic analysis of ES data is a reliable method for pathogenic CNV detection and that it should be incorporated in cases with a negative or inconclusive molecular result after ES.
Keywords: copy number variation; deletion; exome sequencing; retinal dystrophy.
© 2024 The Author(s). Molecular Genetics & Genomic Medicine published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
[Comparison study of whole exome sequencing and targeted panel sequencing in molecular diagnosis of inherited retinal dystrophies].Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2020 Oct 18;52(5):836-844. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2020.05.007. Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2020. PMID: 33047716 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Increasing the yield in targeted next-generation sequencing by implicating CNV analysis, non-coding exons and the overall variant load: the example of retinal dystrophies.PLoS One. 2013 Nov 12;8(11):e78496. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0078496. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24265693 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of New Copy Number Variation and the Evaluation of a CNV Detection Tool for NGS Panel Data in Polish Familial Hypercholesterolemia Patients.Genes (Basel). 2022 Aug 10;13(8):1424. doi: 10.3390/genes13081424. Genes (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36011335 Free PMC article.
-
Free-access copy-number variant detection tools for targeted next-generation sequencing data.Mutat Res Rev Mutat Res. 2019 Jan-Mar;779:114-125. doi: 10.1016/j.mrrev.2019.02.005. Epub 2019 Feb 23. Mutat Res Rev Mutat Res. 2019. PMID: 31097148 Review.
-
Scaling New Heights in the Genetic Diagnosis of Inherited Retinal Dystrophies.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2019;1185:215-219. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-27378-1_35. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2019. PMID: 31884614 Review.
References
-
- Bauwens, M. , Garanto A., Sangermano R., et al. 2019. “ABCA4‐Associated Disease as a Model for Missing Heritability in Autosomal Recessive Disorders: Novel Noncoding Splice, Cis‐Regulatory, Structural, and Recurrent Hypomorphic Variants.” Genetics in Medicine: Official Journal of the American College of Medical Genetics 21, no. 8: 1761–1771. 10.1038/s41436-018-0420-y. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

