Doxepin as OCT2 inhibitor ameliorates inflammatory response and modulates PI3K/Akt signaling associated with cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity in rats
- PMID: 39400714
- PMCID: PMC11978677
- DOI: 10.1007/s00210-024-03473-1
Doxepin as OCT2 inhibitor ameliorates inflammatory response and modulates PI3K/Akt signaling associated with cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity in rats
Abstract
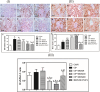
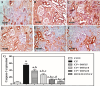
Organic cationic transporter 2 (OCT2) was identified as the main transporter involved in the accumulation of cisplatin (CP) in the proximal tubular renal cells, resulting in nephrotoxicity. Doxepin (DOX) is a tricyclic agent with an inhibitory effect on OCT2. This study aimed to explore the possible mechanisms of the renoprotective role of DOX toward CP-induced nephrotoxicity. Rats were randomly divided into six groups: group 1, control; group 2, CP; groups 3, 4, and 5 were treated with graded doses of DOX (5, 10, and 20 mg/kg, respectively) intraperitoneally (ip) once daily for 10 consecutive days and group 6 was treated only with DOX (20 mg/kg). On the seventh day, a single injected dose of CP (10 mg/kg, ip) was given to the rats in groups 2-5. Seventy-two hours after CP injection, rats were sacrificed, and the kidneys were removed for histological and biochemical measurements. DOX ameliorated the CP-induced histopathological alterations. DOX significantly reduced the expression of OCT2, lipid peroxidation marker (MDA), and inflammatory cytokines, including TNF-α, IL-6, IL-1, IL-2, and IL-1β, and increased the activity of antioxidant enzymes. In addition, pre- and co-treatment with DOX significantly reduced the CP-mediated apoptotic effect by reducing the renal tissue expression of BAX and caspase-3 levels, upregulating the expression of Bcl-2, and modulating the phosphorylation of PI3K/Akt signaling cascade. DOX exerts a nephroprotective impact against CP-mediated nephrotoxicity via the inhibition of OCT2, suppression of inflammation, oxidative stress, and apoptotic markers, and modulation of PI3K/Akt signaling cascade.
Keywords: Apoptosis; Cisplatin; Doxepin; OCT2; PI3K/Akt.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable. Informed consent: Not applicable. Research involving animals: This study was carried out according to the “Guidelines of the Animal Care and Use of Laboratory Animals” and in parallel with the guidelines adopted by the Research Committee at Suez Canal University (approval no. 201911PHDA2). Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Ciarimboli G (2014) Membrane transporters as mediators of cisplatin side-effects. Anticancer Res 34(1):547–550 - PubMed
-
- Culling CFA (1974) Handbook of histopathological and histochemical techniques: including museum techniques. Butterworth-Heinemann. 10.1016/C2013-0-04011-X
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

