Study on the mechanism of echinacoside in preventing and treating hypoxic pulmonary hypertension based on proteomic analyses
- PMID: 39401152
- PMCID: PMC11472809
- DOI: 10.1002/prp2.70025
Study on the mechanism of echinacoside in preventing and treating hypoxic pulmonary hypertension based on proteomic analyses
Abstract
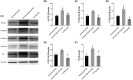
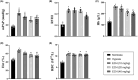
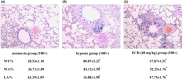
Hypoxic pulmonary hypertension (HPH), a chronic condition affecting the cardiopulmonary system, has high mortality. Echinacoside (ECH) is a phenylethanoid glycoside, which is used to ameliorate pulmonary vascular remodeling and pulmonary vasoconstriction in rats. Accordingly, we aimed to explore the mechanism of ECH in preventing and treating HPH. Sprague Dawley rats were housed in a hypobaric hypoxia chamber for 28 days to obtain the HPH model. The experimental rats were randomly allocated into the following several groups: normoxia group, chronic hypoxia group, and ECH group. The therapeutic results of ECH (10, 20, and 40 mg/kg) showed that ECH reduced mPAP, Hb, Hct, and RVHI in HPH rats. Then this work employed label-free quantitative proteomic analysis, western blotting, and RT-PCR to investigate the mechanism by which ECH prevents HPH. The results found that in the chronic hypoxia group, the levels of ACSL1, COL6A1, COL4A2, COL1A1, and PC increased compared to the normoxia group. However, the opposite effect was observed in the chronic hypoxia group treated with ECH. The study indicates that the administration of ECH may slow the pathological progression of HPH by suppressing the inflammatory response, inhibiting smooth muscle cell proliferation, and minimizing the deposition of extracellular matrix.
Keywords: cell proliferation; echinacoside; hypoxic pulmonary hypertension; inflammation; proteomics.
© 2024 The Author(s). Pharmacology Research & Perspectives published by British Pharmacological Society and American Society for Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- Veith C, Vartürk‐Özcan I, Wujak M, et al. SPARC, a novel regulator of vascular cell function in pulmonary hypertension. Circulation. 2022;145:916‐933. - PubMed
-
- Humbert M, Kovacs G, Hoeper MM, et al. 2022 ESC/ERS guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary hypertension. Eur Heart J. 2022;43:3618‐3731. - PubMed
-
- Ruopp NF, Cockrill BA. Diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension: a review. JAMA. 2022;327:1379. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

