Hypothalamic tanycytes internalize ghrelin from the cerebrospinal fluid: Molecular mechanisms and functional implications
- PMID: 39401613
- PMCID: PMC11532763
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molmet.2024.102046
Hypothalamic tanycytes internalize ghrelin from the cerebrospinal fluid: Molecular mechanisms and functional implications
Abstract
Objective: The peptide hormone ghrelin exerts potent effects in the brain, where its receptor is highly expressed. Here, we investigated the role of hypothalamic tanycytes in transporting ghrelin across the blood-cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) interface.
Methods: We investigated the internalization and transport of fluorescent ghrelin (Fr-ghrelin) in primary cultures of rat hypothalamic tanycytes, mouse hypothalamic explants, and mice. We also tested the impact of inhibiting clathrin-mediated endocytosis of ghrelin in the brain ventricular system on the orexigenic and locomotor effects of the hormone.
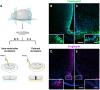
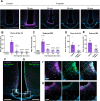
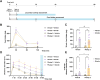
Results: In vitro, we found that Fr-ghrelin is selectively and rapidly internalized at the soma of tanycytes, via a GHSR-independent and clathrin-dependent mechanism, and then transported to the endfoot. In hypothalamic explants, we also found that Fr-ghrelin is internalized at the apical pole of tanycytes. In mice, Fr-ghrelin present in the CSF was rapidly internalized by hypothalamic β-type tanycytes in a clathrin-dependent manner, and pharmacological inhibition of clathrin-mediated endocytosis in the brain ventricular system prolonged the ghrelin-induced locomotor effects.
Conclusions: We propose that tanycyte-mediated transport of ghrelin is functionally relevant, as it may contribute to reduce the concentration of this peptide hormone in the CSF and consequently shortens the duration of its central effects.
Keywords: Blood-cerebro spinal barrier; Hypothalamus; Locomotor activity.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier GmbH.. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

