Clustering lysosomes around the MTOC: a promising strategy for SNCA/alpha-synuclein breakdown leading to parkinson disease treatment
- PMID: 39401987
- PMCID: PMC11587859
- DOI: 10.1080/15548627.2024.2413295
Clustering lysosomes around the MTOC: a promising strategy for SNCA/alpha-synuclein breakdown leading to parkinson disease treatment
Abstract
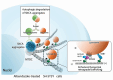
Macroautophagy/autophagy maintains cellular homeostasis by degrading cytoplasmic components and its disruption is linked to Parkinson disease (PD), which is characterized by dopamine depletion and the accumulation of SNCA/α-synuclein aggregates in neurons. Therefore, activation of autophagy is considered a therapeutic strategy for PD; however, autophagy inducers have not yet been developed as therapeutic drugs because they are involved in a wide range of signaling pathways. Here, we focused on the lysosomal clustering around the microtubule-organizing center (MTOC) that can regulate the process of autophagosome-lysosome fusion, the final step of autophagy, and examined how lysosomal clustering affects protein degradation through autophagy. Our study identified six compounds from a high-content screen of 1,200 clinically approved drugs that induce both lysosomal clustering and autophagy. Notably, albendazole reduced SNCA aggregates in a PD model by lysosomal clustering and autophagy. These findings suggest that targeting lysosomal clustering could offer new therapeutic insights for PD.
Keywords: Alpha-synuclein; Parkinson disease; autophagy; lysosomal clustering; lysosomal trafficking.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous