Pre-operative stereotactic radiosurgery and peri-operative dexamethasone for resectable brain metastases: a two-arm pilot study evaluating clinical outcomes and immunological correlates
- PMID: 39402027
- PMCID: PMC11473782
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-53034-6
Pre-operative stereotactic radiosurgery and peri-operative dexamethasone for resectable brain metastases: a two-arm pilot study evaluating clinical outcomes and immunological correlates
Abstract
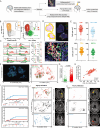
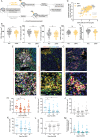
Enhancing the efficacy of immunotherapy in brain metastases (BrM) requires an improved understanding of the immune composition of BrM and how this is affected by radiation and dexamethasone. Our two-arm pilot study (NCT04895592) allocated 26 patients with BrM to either low (Arm A) or high (Arm B) dose peri-operative dexamethasone followed by pre-operative stereotactic radiosurgery (pSRS) and resection (n= 13 per arm). The primary endpoint, a safety analysis at 4 months, was met. The secondary clinical endpoints of overall survival, distant brain failure, leptomeningeal disease and local recurrence at 12-months were 66%, 37.3%, 6%, and 0% respectively and were not significantly different between arms (p= 0.7739, p= 0.3884, p= 0.3469). Immunological data from two large retrospective BrM datasets and confirmed by correlates from both arms of this pSRS prospective trial revealed that BrM CD8 T cells were composed of predominantly PD1+ TCF1+ stem-like and PD1+ TCF1-TIM3+ effector-like cells. Clustering of TCF1+ CD8 T cells with antigen presenting cells in immune niches was prognostic for local control, even without pSRS. Following pSRS, CD8 T cell and immune niche density were transiently reduced compared to untreated BrM, followed by a rebound 6+ days post pSRS with an increased frequency of TCF1- effector-like cells. In sum, pSRS is safe and therapeutically beneficial, and these data provide a framework for how pSRS may be leveraged to maximize intracranial CD8 T cell responses.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



Update of
-
Immune niches in brain metastases contain TCF1+ stem-like T cells, are associated with disease control and are modulated by preoperative SRS.Res Sq [Preprint]. 2023 Mar 23:rs.3.rs-2722744. doi: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-2722744/v1. Res Sq. 2023. Update in: Nat Commun. 2024 Oct 14;15(1):8854. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-53034-6. PMID: 36993444 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Naito, Y. et al. CD8+ T cells infiltrated within cancer cell nests as a prognostic factor in human colorectal cancer. Cancer Res. 58, 3491–3494 (1998). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

