Surface tension enables induced pluripotent stem cell culture in commercially available hardware during spaceflight
- PMID: 39402072
- PMCID: PMC11473755
- DOI: 10.1038/s41526-024-00435-y
Surface tension enables induced pluripotent stem cell culture in commercially available hardware during spaceflight
Abstract
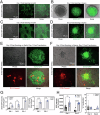
Low Earth Orbit (LEO) has emerged as a unique environment for evaluating altered stem cell properties in microgravity. LEO has become increasingly accessible for research and development due to progress in private spaceflight. Axiom Mission 2 (Ax-2) was launched as the second all-private astronaut mission to the International Space Station (ISS). Frozen human induced pluripotent stem cells (hiPSCs) expressing green fluorescent protein (GFP) under the SOX2 promoter, as well as fibroblasts differentiated from SOX2-GFP hiPSCs, were sent to the ISS. Astronauts then thawed and seeded both cell types into commercially available 96-well plates, which provided surface tension that reduced fluid movement out of individual wells and showed that hiPSCs or hiPSC-derived fibroblasts could survive either in suspension or attached to a Matrigel substrate. Furthermore, both cell types could be transfected with red fluorescent protein (RFP)-expressing plasmid. We demonstrate that hiPSCs and hiPSC-fibroblasts can be thawed in microgravity in off-the-shelf, commercially-available cell culture hardware, can associate into 3D spheroids or grow adherently in Matrigel, and can be transfected with DNA. This lays the groundwork for future biomanufacturing experiments in space.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
M.M. (none). M.A. (none). P.M. (employee of Axiom Space, Inc.). D.M.N.M. (employee of BioServe Space Technologies). S.P. (none). George Lawless (none). S.D. (employee of BioServe Space Technologies). S.A.N. (none). R.B. (none). A.A.Q. (none). P.W. (employee of Axiom Space, Inc.). J.S. (none). Jana Stoudemire (employee of Axiom Space, Inc.). S.C. (employee of BioServe Space Technologies). C.S. (none). Arun Sharma (none).
Figures



References
-
- Arzt, M., Mozneb, M., Escopete, S., Moses, J. & Sharma, A. The benefits of stem cell biology and tissue engineering in low-earth orbit. Stem Cells Dev.33, 143-147 (2024) - PubMed
-
- Chua, C. Y. X. et al. Advanced material technologies for space and terrestrial medicine. Nat. Rev. Mater.10.1038/s41578-024-00691-0. (2024)
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

