Nrf-2/HO-1 activation protects against oxidative stress and inflammation induced by metal welding fume UFPs in 16HBE cells
- PMID: 39402078
- PMCID: PMC11473639
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-74599-8
Nrf-2/HO-1 activation protects against oxidative stress and inflammation induced by metal welding fume UFPs in 16HBE cells
Abstract
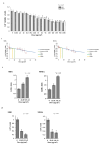
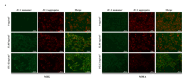
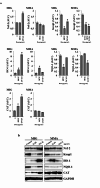
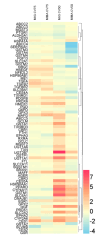
As one of the main occupational hazards, welding fumes can cause oxidative damage and induce series of diseases, such as COPD or asthma. To clarify the effects of the metal fume ultrafine particulates (MF-UFPs) of welding fumes on oxidative damage, UFPs were collected by melt inert gas (MIG) and manual metal arc (MMA) welding, and the composition was confirmed. Human bronchial epithelial 16HBE cells were treated with 0-1000 µg/cm2 MF-UFPs to analyse the cytotoxicity, oxidative stress and cytokines. The protein and mRNA expression of Keap1-Nrf-2/antioxidant response elements (AREs) signalling pathway components were also analysed. After 4 h of treatment, the cell viability decreased 25% after 33.85 and 32.81 µg/cm2 MIG/MMA-UFPs treated. The intracellular ATP concentrations were also decreased significantly, while LDH leakage was increased. The decreased mitochondrial membrane potential and increased ROS suggested the occurrence of oxidative damage, and the results of proteome profiling arrays also showed a significant increase in IL-6 and IL-8. The expression of AREs which related to antioxidant and anti-inflammatory were also increased. These results indicate that the MF-UFPs can cause oxidative stress in 16HBE cells and activate the Nrf-2/ARE signalling pathway to against oxidative damage.
Keywords: Nrf-2/ARE; Oxidative stress; Ultrafine particles; Welding fume.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 202140489/Shanghai Municipal Health Commission
- GWVI-11.2-YQ34/Three-year action plan of Shanghai Public Health System Construction
- GWVI-11.1-41/Three-year action plan of Shanghai Public Health System Construction
- 21YF1439100/Shanghai Sailing Program
- SEPKL-EHIAEC-202204/Special fund of State Environmental Protection Key Laboratory of Environmental Health Impact Assessment of Emerging Contaminants
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

