CCL2-mediated endothelial injury drives cardiac dysfunction in long COVID
- PMID: 39402206
- PMCID: PMC12243935
- DOI: 10.1038/s44161-024-00543-8
CCL2-mediated endothelial injury drives cardiac dysfunction in long COVID
Abstract
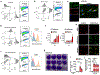
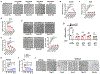
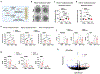
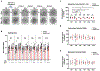
Evidence linking the endothelium to cardiac injury in long coronavirus disease (COVID) is well documented, but the underlying mechanisms remain unknown. Here we show that cytokines released by endothelial cells (ECs) contribute to long-COVID-associated cardiac dysfunction. Using thrombotic vascular tissues from patients with long COVID and induced pluripotent stem cell-derived ECs (iPSC-ECs), we modeled endotheliitis and observed similar dysfunction and cytokine upregulation, notably CCL2. Cardiac organoids comprising iPSC-ECs and iPSC-derived cardiomyocytes showed cardiac dysfunction after severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) exposure, driven by CCL2. Profiling of chromatin accessibility and gene expression at a single-cell resolution linked CCL2 to 'phenotype switching' and cardiac dysfunction, validated by high-throughput proteomics. Disease modeling of cardiac organoids and exposure of human ACE2 transgenic mice to SARS-CoV-2 spike proteins revealed that CCL2-induced oxidative stress promoted post-translational modification of cardiac proteins, leading to cardiac dysfunction. These findings suggest that EC-released cytokines contribute to cardiac dysfunction in long COVID, highlighting the importance of early vascular health monitoring in patients with long COVID.
© 2024. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature Limited.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests
J.C.W. is a founder of Greenstone Biosciences but has no competing interests as the work presented here was performed independently. The other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures













References
-
- Al-Aly Z, Xie Y & Bowe B High-dimensional characterization of post-acute sequelae of COVID-19. Nature 594, 259–264 (2021). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- K99 HL163443-01/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI)
- 869015/American Heart Association (American Heart Association, Inc.)
- R01 HL161002/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K01 HL135455/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL150693/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
