Developmental and validation of a novel small and high-efficient panel of microhaplotypes for forensic genetics by the next generation sequencing
- PMID: 39402483
- PMCID: PMC11475632
- DOI: 10.1186/s12864-024-10880-4
Developmental and validation of a novel small and high-efficient panel of microhaplotypes for forensic genetics by the next generation sequencing
Abstract
Background: In the domain of forensic science, the application of kinship identification and mixture deconvolution techniques are of critical importance, providing robust scientific evidence for the resolution of complex cases. Microhaplotypes, as the emerging class of genetic markers, have been widely studied in forensics due to their high polymorphisms and excellent stability.
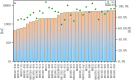
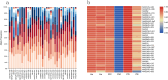
Results and discussion: In this research, a novel and high-efficient panel integrating 33 microhaplotype loci along with a sex-determining locus was developed by the next generation sequencing technology. In addition, we also assessed its forensic utility and delved into its capacity for kinship analysis and mixture deconvolution. The average effective number of alleles (Ae) of the 33 microhaplotype loci in the Guizhou Han population was 6.06, and the Ae values of 30 loci were greater than 5. The cumulative power of discrimination and cumulative power of exclusion values of the novel panel in the Guizhou Han population were 1-5.6 × 10- 43 and 1-1.6 × 10- 15, respectively. In the simulated kinship analysis, the panel could effectively distinguish between parent-child, full-sibling, half-sibling, grandfather-grandson, aunt-nephew and unrelated individuals, but uncertainty rates clearly increased when distinguishing between first cousins and unrelated individuals. For the mixtures, the novel panel had demonstrated excellent performance in estimating the number of contributors of mixtures with 1 to 5 contributors in combination with the machine learning methods.
Conclusions: In summary, we have developed a small and high-efficient panel for forensic genetics, which could provide novel insights into forensic complex kinships testing and mixture deconvolution.
Keywords: Complex kinships; Forensic genetics; Guizhou Han; Microhaplotype; Next generation sequencing.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





References
-
- Tao RY, Dong XY, Chen AQ, Lü YH, Zhang SH, Li CT. Application progress of massively parallel sequencing technology in STR genetic marker detection. Fa Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2022;38(2):267–79. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

