The severity assessment and nucleic acid turning-negative-time prediction in COVID-19 patients with COPD using a fused deep learning model
- PMID: 39402509
- PMCID: PMC11476205
- DOI: 10.1186/s12890-024-03333-x
The severity assessment and nucleic acid turning-negative-time prediction in COVID-19 patients with COPD using a fused deep learning model
Abstract
Background: Previous studies have shown that patients with pre-existing chronic obstructive pulmonary diseases (COPD) were more likely to be infected with coronavirus disease (COVID-19) and lead to more severe lung lesions. However, few studies have explored the severity and prognosis of COVID-19 patients with different phenotypes of COPD.
Purpose: The aim of this study is to investigate the value of the deep learning and radiomics features for the severity evaluation and the nucleic acid turning-negative time prediction in COVID-19 patients with COPD including two phenotypes of chronic bronchitis predominant patients and emphysema predominant patients.
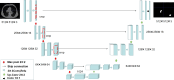
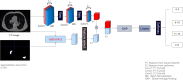
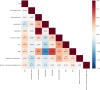
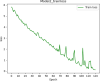
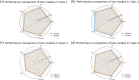
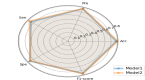
Methods: A total of 281 patients were retrospectively collected from Hohhot First Hospital between October 2022 and January 2023. They were divided to three groups: COVID-19 group of 95 patients, COVID-19 with emphysema group of 94 patients, COVID-19 with chronic bronchitis group of 92 patients. All patients underwent chest computed tomography (CT) scans and recorded clinical data. The U-net model was pretrained to segment the pulmonary involvement area on CT images and the severity of pneumonia were evaluated by the percentage of pulmonary involvement volume to lung volume. The 107 radiomics features were extracted by pyradiomics package. The Spearman method was employed to analyze the correlation of the data and visualize it through a heatmap. Then we establish a deep learning model (model 1) and a fusion model (model 2) combined deep learning with radiomics features to predict nucleic acid turning-negative time.
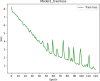
Results: COVID-19 patients with emphysema was lowest in the lymphocyte count compared to COVID-19 patients and COVID-19 companied with chronic bronchitis, and they have the most extensive range of pulmonary inflammation. The lymphocyte count was significantly correlated with pulmonary involvement and the time for nucleic acid turning negative (r=-0.145, P < 0.05). Importantly, our results demonstrated that model 2 achieved an accuracy of 80.9% in predicting nucleic acid turning-negative time.
Conclusion: The pre-existing emphysema phenotype of COPD severely aggravated the pulmonary involvement of COVID-19 patients. Deep learning and radiomics features may provide more information to accurately predict the nucleic acid turning-negative time, which is expected to play an important role in clinical practice.
Keywords: COVID-19 with COPD; Deep learning method; Nucleic acid turning-negative time; Pulmonary involvement; Radiomics features.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- 2023YFSH0015/the Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region Science and Technology Plan Project
- 2023YFSH0015/the Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region Science and Technology Plan Project
- 2023YFSH0015/the Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region Science and Technology Plan Project
- 2023YFSH0015/the Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region Science and Technology Plan Project
- 2023YFSH0015/the Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region Science and Technology Plan Project
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

