Serum MicroRNAs as Predictors of Diagnosis and Drug-resistance in Temporal Lobe Epilepsy: A Preliminary Study
- PMID: 39403059
- PMCID: PMC11451323
- DOI: 10.2174/1570159X22666240516145823
Serum MicroRNAs as Predictors of Diagnosis and Drug-resistance in Temporal Lobe Epilepsy: A Preliminary Study
Abstract
Objective: Temporal lobe epilepsy (TLE) is the most common form of refractory focal epilepsy, and the current clinical diagnosis is based on EEG, clinical neurological history and neuroimaging findings.
Methods: So far, there are no blood-based molecular biomarkers of TLE to support clinical diagnosis, despite the pathogenic mechanisms underlying TLE involving defects in the regulation of gene expression. MicroRNAs (miRNAs) have emerged as important post-transcriptional regulators of gene expression.
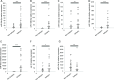
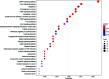
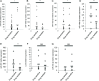
Results: Recent studies show the feasibility of detecting miRNAs in body fluids; circulating miRNAs have emerged as potential clinical biomarkers in epilepsy, although the TLE miRNA profile needs to be addressed. Here, we analysed the diagnostic potential of 8 circulating miRNAs in sera of 52 TLE patients and 40 age- and sex-matched donor controls by RT-qPCR analyses.
Conclusion: We found that miR-34a-5p, -106b-5p, -130a-3p, -146a-5p, and -19a-3p are differently expressed in TLE compared to control subjects, suggesting a diagnostic role. Furthermore, we found that miR-34a-5p, -106b-5p, -146a-5p and miR-451a could become prognostic biomarkers, being differentially expressed between drug-resistant and drug-responsive TLE subjects. Therefore, serum miRNAs are diagnostic and drug-resistance predictive molecules of TLE.
Keywords: TLE; Temporal lobe epilepsy; circulating biomarkers.; diagnosis; miRNAs; microRNAs; prediction of therapy response; prognosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest, financial or otherwise.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
