Cerebrovascular disease is associated with Alzheimer's plasma biomarker concentrations in adults with Down syndrome
- PMID: 39403075
- PMCID: PMC11472828
- DOI: 10.1093/braincomms/fcae331
Cerebrovascular disease is associated with Alzheimer's plasma biomarker concentrations in adults with Down syndrome
Abstract
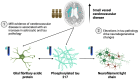
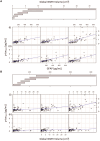
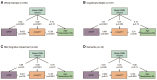
By age 40 years, over 90% of adults with Down syndrome have Alzheimer's disease pathology and most progress to dementia. Despite having few systemic vascular risk factors, individuals with Down syndrome have elevated cerebrovascular disease markers that track with the clinical progression of Alzheimer's disease, suggesting a role of cerebrovascular disease that is hypothesized to be mediated by inflammatory factors. This study examined the pathways through which small vessel cerebrovascular disease contributes to Alzheimer's disease-related pathophysiology and neurodegeneration in adults with Down syndrome. One hundred eighty-five participants from the Alzheimer's Biomarkers Consortium-Down Syndrome [mean (SD) age = 45.2 (9.3) years] with available MRI and plasma biomarker data were included in this study. White matter hyperintensity (WMH) volumes were derived from T2-weighted fluid-attenuated inversion recovery MRI scans, and plasma biomarker concentrations of amyloid beta 42/40, phosphorylated tau 217, astrocytosis (glial fibrillary acidic protein) and neurodegeneration (neurofilament light chain) were measured with ultrasensitive immunoassays. We examined the bivariate relationships of WMH, amyloid beta 42/40, phosphorylated tau 217 and glial fibrillary acidic protein with age-residualized neurofilament light chain across Alzheimer's disease diagnostic groups. A series of mediation and path analyses examined statistical pathways linking WMH and Alzheimer's disease pathophysiology to promote neurodegeneration in the total sample and groups stratified by clinical diagnosis. There was a direct and indirect bidirectional effect through the glial fibrillary acidic protein of WMH on phosphorylated tau 217 concentration, which was associated with neurofilament light chain concentration in the entire sample. Amongst cognitively stable participants, WMH was directly and indirectly, through glial fibrillary acidic protein, associated with phosphorylated tau 217 concentration, and in those with mild cognitive impairment, there was a direct effect of WMH on phosphorylated tau 217 and neurofilament light chain concentrations. There were no associations of WMH with biomarker concentrations among those diagnosed with dementia. The findings from this cross-sectional study suggest that among individuals with Down syndrome, cerebrovascular disease promotes neurodegeneration by increasing astrocytosis and tau pathophysiology in the presymptomatic phases of Alzheimer's disease, but future studies will need to confirm these associations with longitudinal data. This work joins an emerging literature that implicates cerebrovascular disease and its interface with neuroinflammation as a core pathological feature of Alzheimer's disease in adults with Down syndrome.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; Down syndrome; biomarkers; cerebrovascular disease; magnetic resonance imaging.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Guarantors of Brain.
Conflict of interest statement
O.H. has received consulting fees for AC Immune, Amylyx, ALZpath, BioArctic, Biogen, Cerveau, Eisai, Eli Lilly, Fujirebio, Merck, Novartis, Novo Nordisk, Roche, Sanofi and Siemens; S.Z. has received consulting fees from Lundbeck; D.M.W. has received consulting fees from Biohaven Therapeutics; E.H. has received consulting fees for Alzheon and Cyclo Therapeutics; A.M.B. has received consulting fees from Cogstate, Cognito Therapeutics, IQVIA, and Cognition Therapeutics.
Figures

Update of
-
Cerebrovascular disease drives Alzheimer plasma biomarker concentrations in adults with Down syndrome.medRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Nov 30:2023.11.28.23298693. doi: 10.1101/2023.11.28.23298693. medRxiv. 2023. Update in: Brain Commun. 2024 Sep 25;6(5):fcae331. doi: 10.1093/braincomms/fcae331. PMID: 38076904 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Head E, Lott IT.. Down syndrome and beta-amyloid deposition. Curr Opin Neurol. 2004;17(2):95–100. - PubMed
-
- de Graaf G, Buckley F, Skotko BG. Estimation of the number of people with Down syndrome in the United States. Genet Med. 2017;19(4):439–447. - PubMed
-
- NIA-AA Revised Criteria for Diagnosis and Staging of Alzheimer's Disease. 2023:38. 2023. https://alz.org/media/Documents/scientific-conferences/NIA-AA-Clinical-C....
Grants and funding
- P30 AG066444/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG005681/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U54 HD087011/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG066462/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 HD105353/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG051412/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG005133/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001414/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR002373/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- F31 AG090091/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG062715/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U54 HD090256/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR002345/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001857/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U24 AG021886/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG062421/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG008702/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG066519/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U19 AG068054/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R00 AG065506/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG051406/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001873/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
