SNPs in cytochromes P450 catalyzing cholesterol degradation in brain are associated with Parkinson's disease
- PMID: 39403150
- PMCID: PMC11472000
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1477009
SNPs in cytochromes P450 catalyzing cholesterol degradation in brain are associated with Parkinson's disease
Abstract
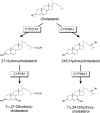
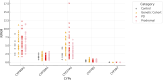
Besides being an essential structural component of plasma membranes and the precursor of many functional compounds and signaling molecules, cholesterol was also proposed to play a role in the etiology and/or manifestation of Parkinson's disease (PD). However, so far systematic investigations on the role of cholesterol and its metabolites present in the brain for the etiology of PD are missing. Here, we investigate for the first time the association of PD with SNPs in the genes of four cytochromes P450 (P450), CYP46A1, CYP39A1, CYP27A1 and CYP7B1, which are critical for the degradation of cholesterol in the brain. Analyzing 1,349 individuals from the PPMI data base, we found 24 SNPs in these four genes, which are significantly over- or under-represented in patients suffering from idiopathic PD (IPD). Studying each of the 362 IPD patients individually, we found that most patients (45%) showed only one associated SNP in one of the four P450 genes, while 31% displayed two associated SNPs and 18% three associated SNPs. The occurrence of some associated SNPs is in the same order of magnitude as SNPs in the GBA (beta-glucocerebrosidase) and thus might reflect a genetic predisposition for PD. As all 24 SNPs were located in introns and 3' untranslated regions, we evaluated the prospective regulatory impact of the surrounding genomic regions by using transcriptome and epigenome data from the Foundational Data Initiative for Parkinson Disease (FOUNDIN-PD). FOUNDIN-PD provides gene expression, open chromatin and DNA methylation data in a cohort of 89 induced pluripotent stem cell (iPSC) lines differentiated to dopaminergic (DA) neurons derived from people in the PPMI study. Indeed, two of the 24 SNPs, one in CYP7B1 (rs118111353) and the other one in CYP27A1 (rs74446825), were localized within a region of open chromatin in differentiated neurons. Interestingly, all iPSC lines with open chromatin in rs118111353 showed the reference allele. As all four P450, CYP46A1, CYP39A1, CYP27A1 and CYP7B1, are expressed in dopaminergic neurons, we discuss further functional studies to connect SNPs in regulatory regions with gene expression levels. Finally, potential possibilities for personalized therapeutic treatment of patients with SNPs in the four investigated P450 are discussed.
Keywords: CYP27A1; CYP39A1; CYP46A1; CYP7B1; Parkinson's disease; cholesterol; cytochromes P450.
Copyright © 2024 Petkova-Kirova, Kolchina, Baas, Wagenpfeil, Unger, Schulze-Hentrich and Bernhardt.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

