The effect of childhood trauma on moral cognition in patients with schizophrenia
- PMID: 39403323
- PMCID: PMC11471594
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyt.2024.1432407
The effect of childhood trauma on moral cognition in patients with schizophrenia
Abstract
Objective: The aim of this study was to investigate whether a potential moral cognitive impairment (failure in understanding moral rules) exists in patients with schizophrenia (SCZ) and to explore the effect of childhood trauma (CT) on moral cognition in a group of patients with SCZ.
Methods: A total of 99 patients with SCZ and 102 healthy controls (HCs) were included in this study. The Childhood Trauma Questionnaire-Short Form (CTQ) was administered to assess childhood trauma experiences in both groups, while the Moral Identity Measure (MIM) and the Moral Foundations Questionnaire (MFQ) were applied for a comparative evaluation of moral cognition across the two groups. The Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale (PANSS) was administered to assess the psychopathology.
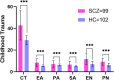
Results: Patients with schizophrenia had significantly greater CTQ scores than HCs (42.77 ± 13.50 vs. 29.11 ± 4.25, t=9.697, p<0.001). The prevalence of childhood trauma (χ 2 = 58.452, p<0.001) and history of aggressive behaviors (χ 2 = 23.565, p=0.001) among patients with SCZ were greater than that among HCs. In addition, the scores of moral cognition (MIM: 61.82 ± 15.12 vs. 70.88 ± 8.87, p=0.001; MFQ: 87.24 ± 22.30 vs. 112.62 ± 23.42, p=0.045) in the SCZ group was lower than that in the HC group after controlling for the influence of CT covariates. The MFQ score was negatively correlated with the CTQ score, the emotional abuse (EA) score, the physical abuse (PA) score and the physical neglect (PN) score in SCZ patients. Among HCs, the MFQ score was positively correlated with the CTQ score, as well as with the dimensions of physical abuse (PA) and emotional Neglect (EN). Multiple linear regression analyses revealed that impaired moral cognition performance was significantly predicted by the CTQ score (beta=-0.235, p=0.034, 95% CI -0.743 to -0.031) in patients with SCZ but was significantly predicted by years of education (beta=-0.392, p<0.001, 95% CI -4.783 to -1.876), alcohol use (beta=0.210, p=0.023, 95% CI 2.191 to 29.399) and the CTQ score (beta=0.184, p=0.046, 95% CI 0.019 to 1.928) in HCs. CTQ moderated the effect of SCZ on MFQ (B = 0.516); Simple tests revealed that the group effect on the MFQ was B=12.306 at the lower level(-1SD) and B = 54.089 at the higher level(+1SD) of the CTQ scores.
Conclusions: SCZ patients exhibit impaired moral cognition. The contribution of CT to the presence of moral cognitive impairments seems to be independent of psychopathology.
Keywords: CTQ; MFQ; childhood trauma; moral cognition; schizophrenia.
Copyright © 2024 Peng, Ding, Ren, Zhao, Wang, Zhao, Zhang, Zhang, Zhou and Wang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

