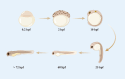
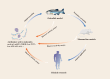
Advantages of the zebrafish tumor xenograft model: the evaluation of efficacy in cancer therapy and the application to the study of lncRNAs
- PMID: 39403375
- PMCID: PMC11471560
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1483192
Advantages of the zebrafish tumor xenograft model: the evaluation of efficacy in cancer therapy and the application to the study of lncRNAs
Abstract
In the current preclinical anti-tumor researches, there is a general lack of an in vivo model that can quickly and efficiently screen effective anti-tumor drugs. As a species that is 87% genetically similar to humans, zebrafish have been widely used to model human diseases, and they are considered an alternative economic model for studying cancer development, proliferation, and metastasis. The zebrafish tumor xenograft model has been effectively used for cancer drug development at all levels, including target validation, and high-throughput screening of long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) that may be involved in tumor regulation. In this review, we provide a comprehensive overview of zebrafish as an in vivo model for cancer cell growth, migration, anti-tumor immunotherapy, and anti-tumor drug screening. In addition, the regulatory mechanisms of some active lncRNAs have been identified to play a role in the pathogenesis of cancer, but it is still necessary to take advantage of the efficient zebrafish model to screen and learn more about the role of these molecules in tumor development and migration. Current anti-tumor therapies are limited by severe toxicity and multidrug resistance. There is an urgent need for the cost-effective and efficient in vivo research tools to improve our understanding and overcome these problems. This paper reviews the different purposes of anti-tumor research using zebrafish model. We discuss the use of zebrafish in cancer cell proliferation and metastasis, identifying signaling pathways, cancer drug discovery and treatment development, and toxicity studies. Finally, this review highlights the limitations of the field and future directions to effectively utilize zebrafish as a highly efficient model for cancer treatment development.
Keywords: anti-tumor research; cancer therapy; immunotherapy; lncRNAs; zebrafish model.
Copyright © 2024 Hu, Sun, Chen, Lyu, Yuan and Jiang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials