Competing endogenous RNAs (ceRNAs) and drug resistance to cancer therapy
- PMID: 39403602
- PMCID: PMC11472581
- DOI: 10.20517/cdr.2024.66
Competing endogenous RNAs (ceRNAs) and drug resistance to cancer therapy
Abstract
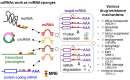
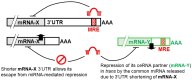
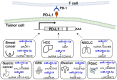
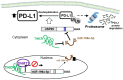
Competing endogenous RNAs (ceRNAs) are transcripts that possess highly similar microRNA response elements (MREs). microRNAs (miRNAs) are short, endogenous, single-stranded non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs) that can repress gene expression by binding to MREs on the 3' untranslated regions (UTRs) of the target mRNA transcripts to suppress gene expression by promoting mRNA degradation and/or inhibiting protein translation. mRNA transcripts, circular RNAs (circRNAs), long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs), and transcribed pseudogenes could share similar MREs, and they can compete for the same pool of miRNAs. These ceRNAs may affect the level of one another by competing for their shared miRNAs. This interplay between different RNAs constitutes a ceRNA network, which regulates many important biological processes. Cancer drug resistance is a major factor leading to treatment failure in patients receiving chemotherapy. It can be acquired through genetic, epigenetic, and various tumor microenvironment mechanisms. The involvement of ceRNA crosstalk and its disruption in chemotherapy resistance is attracting attention in the cancer research community. This review presents an updated summary of the latest research on ceRNA dysregulation causing drug resistance across different cancer types and chemotherapeutic drug classes. Interestingly, accumulating evidence suggests that ceRNAs may be used as prognostic biomarkers to predict clinical response to cancer chemotherapy. Nevertheless, detailed experimental investigations of the putative ceRNA networks generated by computational algorithms are needed to support their translation for therapeutic and prognostic applications.
Keywords: Alternative mRNA polyadenylation; cancer immunotherapy; ceRNA crosstalk; immune evasion; mRNA 3’untranslated region; microRNA; multidrug resistance; non-coding RNA.
© The Author(s) 2024.
Conflict of interest statement
To KKW and Cho WC are Editorial Board members of the journal Cancer Drug Resistance, while the other authors declared that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Competing Endogenous RNAs (ceRNAs) in Colorectal Cancer: A Review.Expert Rev Mol Med. 2022 Jun 24;24:e27. doi: 10.1017/erm.2022.21. Expert Rev Mol Med. 2022. PMID: 35748050 Review.
-
microRNAs and ceRNAs: RNA networks in pathogenesis of cancer.Chin J Cancer Res. 2013 Apr;25(2):235-9. doi: 10.3978/j.issn.1000-9604.2013.03.08. Chin J Cancer Res. 2013. PMID: 23592905 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of ncRNAs as ceRNAs in Gastric Cancer.Genes (Basel). 2021 Jul 2;12(7):1036. doi: 10.3390/genes12071036. Genes (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34356052 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Oncocers: ceRNA-mediated cross-talk by sponging miRNAs in oncogenic pathways.Tumour Biol. 2015 May;36(5):3129-36. doi: 10.1007/s13277-015-3346-x. Epub 2015 Mar 27. Tumour Biol. 2015. PMID: 25809705 Review.
-
Competing endogenous RNAs in lung cancer.Cancer Biol Med. 2021 Feb 15;18(1):1-20. doi: 10.20892/j.issn.2095-3941.2020.0203. Cancer Biol Med. 2021. PMID: 33628581 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
LncRNA16 inhibits pyroptosis and promotes platinum resistance in non-small cell lung cancer by sponging miRNA1827 to regulate MBD3/GSDME expression.Cancer Cell Int. 2025 May 24;25(1):192. doi: 10.1186/s12935-025-03812-z. Cancer Cell Int. 2025. PMID: 40413520 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic and diagnostic value of circRNA expression in cervical cancer: a meta analysis.Front Oncol. 2025 Jan 13;14:1488040. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1488040. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2025. PMID: 39871946 Free PMC article.
-
A novel role of miR-223-3p in reducing NLRP3-mediated inflammation and deep vein thrombosis in a mouse model.Sci Prog. 2025 Apr-Jun;108(2):368504251337526. doi: 10.1177/00368504251337526. Epub 2025 Apr 23. Sci Prog. 2025. PMID: 40267315 Free PMC article.
-
Dysregulation of transposable elements and PIWI-interacting RNAs in myelodysplastic neoplasms.Biomark Res. 2025 Jan 23;13(1):13. doi: 10.1186/s40364-025-00725-x. Biomark Res. 2025. PMID: 39849644 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of immune-mediated chemoresistance in cancer by lncRNAs: an in-depth review of signaling pathways.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025 Apr 9. doi: 10.1007/s00210-025-04081-3. Online ahead of print. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40202675 Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
