Host combats porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus infection at non-coding RNAs level
- PMID: 39403796
- PMCID: PMC11492689
- DOI: 10.1080/21505594.2024.2416551
Host combats porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus infection at non-coding RNAs level
Abstract
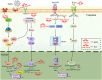
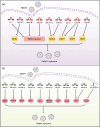
Porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus (PRRSV) poses a significant threat to the global swine industry. The emergence of new, highly virulent strains has precipitated recurrent outbreaks worldwide, underscoring the ongoing battle between host and virus. Thus, there is an imperative to formulate a more comprehensive and effective disease control strategy. Studies have shown that host non-coding RNA (ncRNA) is an important regulator of host - virus interactions in PRRSV infection. Hence, a thorough comprehension of the roles played by ncRNAs in PRRSV infection can augment our understanding of the pathogenic mechanisms underlying PRRSV infection. This review focuses on elucidating contemporary insights into the roles of host microRNAs (miRNAs), long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs), and circular RNAs (circRNAs) in PRRSV infection, providing both theoretical foundations and fresh perspectives for ongoing research into the mechanisms driving PRRSV infection and its pathogenesis.
Keywords: Porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus; circular RNAs; long non-coding RNAs; microRNAs; viral infection.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
