Soluble urine activated leukocyte cell adhesion molecule is a strong predictor of lupus nephritis
- PMID: 39404817
- PMCID: PMC12048083
- DOI: 10.1093/rheumatology/keae559
Soluble urine activated leukocyte cell adhesion molecule is a strong predictor of lupus nephritis
Abstract
Objectives: To evaluate urinary activated leucocyte cell adhesion molecule (ALCAM) and CD6 as predictors of LN progression or disease resolution across a 1-year study.
Methods: Serum and urine samples from biopsy proven LN subjects (n = 122) were prospectively collected over the course of a year at 3- or 6-month intervals (weeks 0, 12, 26 and 52) across multiple study sites and assessed for soluble ALCAM and CD6 levels. Urine creatinine from the same urine sample was used to normalize the levels of urinary ALCAM and urinary CD6. Measured levels of serum and urine ALCAM and CD6 were then analysed against disease metrics cross-sectionally and longitudinally.
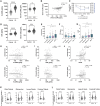
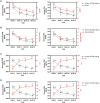
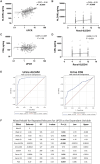
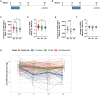
Results: Cross-sectional analysis at baseline revealed that urinary ALCAM significantly correlated with urine protein creatinine ratio, renal SLEDAI, and the Physician Global Assessment (PGA), and negatively correlated with serum C3 and C4. Receiver operating characteristic curve analysis demonstrated that urinary ALCAM is a predictor of LN with an area under the curve (AUC) of 0.97, compared with urinary CD6 with an AUC of 0.71. Importantly, the change in urinary ALCAM over a 3-month period distinguished between non-responders and responders at week 52.
Conclusion: Urinary ALCAM is reflective of changes in LN and may be predictive of response status.
Keywords: ALCAM; CD6; lupus nephritis; urine biomarkers.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the British Society for Rheumatology. All rights reserved. For commercial re-use, please contact reprints@oup.com for reprints and translation rights for reprints. All other permissions can be obtained through our RightsLink service via the Permissions link on the article page on our site—for further information please contact journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures

References
-
- Anders HJ, Saxena R, Zhao MH et al. Lupus nephritis. Nat Rev Dis Primers 2020;6:7. - PubMed
-
- Moroni G, Depetri F, Ponticelli C. Lupus nephritis: when and how often to biopsy and what does it mean? J Autoimmun 2016;74:27–40. - PubMed
-
- Chalmers S, Garcia S, Ampudia J, Ng C, Connelly S, Putterman C, eds. Amelioration of immune complex-mediated glomerulonephritis by CD6 modulation. Atlanta, GA: ACR, 2019.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- UH2 AR067685/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- UM2 AR067678/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- UH2 AR067681/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- UH2 AR067688/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- UH2 AR067689/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- UH2 AR067690/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- UH2 AR067677/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- UH2 AR067694/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- UH2 AR067679/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- UH2 AR067676/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- UH2 AR067691/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- UH2-AR067676/NH/NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

