The current riboswitch landscape in Clostridioides difficile
- PMID: 39405103
- PMCID: PMC11477304
- DOI: 10.1099/mic.0.001508
The current riboswitch landscape in Clostridioides difficile
Abstract
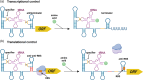
Riboswitches are 5' RNA regulatory elements that are capable of binding to various ligands, such as small metabolites, ions and tRNAs, leading to conformational changes and affecting gene transcription or translation. They are widespread in bacteria and frequently control genes that are essential for the survival or virulence of major pathogens. As a result, they represent promising targets for the development of new antimicrobial treatments. Clostridioides difficile, a leading cause of antibiotic-associated nosocomial diarrhoea in adults, possesses numerous riboswitches in its genome. Accumulating knowledge of riboswitch-based regulatory mechanisms provides insights into the potential therapeutic targets for treating C. difficile infections. This review offers an in-depth examination of the current state of knowledge regarding riboswitch-mediated regulation in C. difficile, highlighting their importance in bacterial adaptability and pathogenicity. Particular attention is given to the ligand specificity and function of known riboswitches in this bacterium. The review also discusses the recent progress that has been made in the development of riboswitch-targeting compounds as potential treatments for C. difficile infections. Future research directions are proposed, emphasizing the need for detailed structural and functional analyses of riboswitches to fully harness their regulatory capabilities for developing new antimicrobial strategies.
Keywords: C. difficile; pathogen; riboswitch; therapeutics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

