Adipocyte lipin 1 expression associates with human metabolic health and regulates systemic metabolism in mice
- PMID: 39405118
- PMCID: PMC11601902
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI169722
Adipocyte lipin 1 expression associates with human metabolic health and regulates systemic metabolism in mice
Abstract
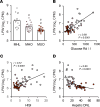
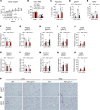
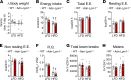
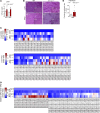
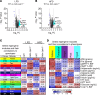
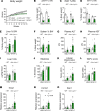
Dysfunctional adipose tissue is believed to promote the development of hepatic steatosis and systemic insulin resistance, but many of the mechanisms involved are still unclear. Lipin 1 catalyzes the conversion of phosphatidic acid to diacylglycerol, the penultimate step of triglyceride synthesis, which is essential for lipid storage. Herein we found that adipose tissue LPIN1 expression is decreased in people with obesity compared with lean subjects, and low LPIN1 expression correlated with multi-tissue insulin resistance and increased rates of hepatic de novo lipogenesis. Comprehensive metabolic and multiomic phenotyping demonstrated that adipocyte-specific Lpin1-/- mice had a metabolically unhealthy phenotype, including liver and skeletal muscle insulin resistance, hepatic steatosis, increased hepatic de novo lipogenesis, and transcriptomic signatures of metabolically associated steatohepatitis that was exacerbated by high-fat diets. We conclude that adipocyte lipin 1-mediated lipid storage is vital for preserving adipose tissue and systemic metabolic health, and its loss predisposes mice to metabolically associated steatohepatitis.
Keywords: Diabetes; Hepatology; Insulin signaling; Metabolism; Obesity.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Update of
-
Adipocyte lipin 1 is positively associated with metabolic health in humans and regulates systemic metabolism in mice.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Feb 3:2023.02.01.526676. doi: 10.1101/2023.02.01.526676. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: J Clin Invest. 2024 Oct 15;134(23):e169722. doi: 10.1172/JCI169722. PMID: 36778276 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- S10 OD027006/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK056341/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R42 DK121652/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK020593/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK020572/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK104735/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U24 DK059637/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL119225/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K01 DK126990/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K01 DK137050/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P20 GM144269/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK020579/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK052574/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DP5 OD028125/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR002345/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- R35 ES028365/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

