Synergistic Effect of Cobalt/Ferrocene as a Catalyst for the Oxygen Evolution Reaction
- PMID: 39405490
- PMCID: PMC12303365
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.jpclett.4c02039
Synergistic Effect of Cobalt/Ferrocene as a Catalyst for the Oxygen Evolution Reaction
Abstract
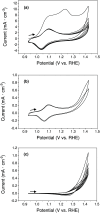
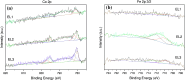
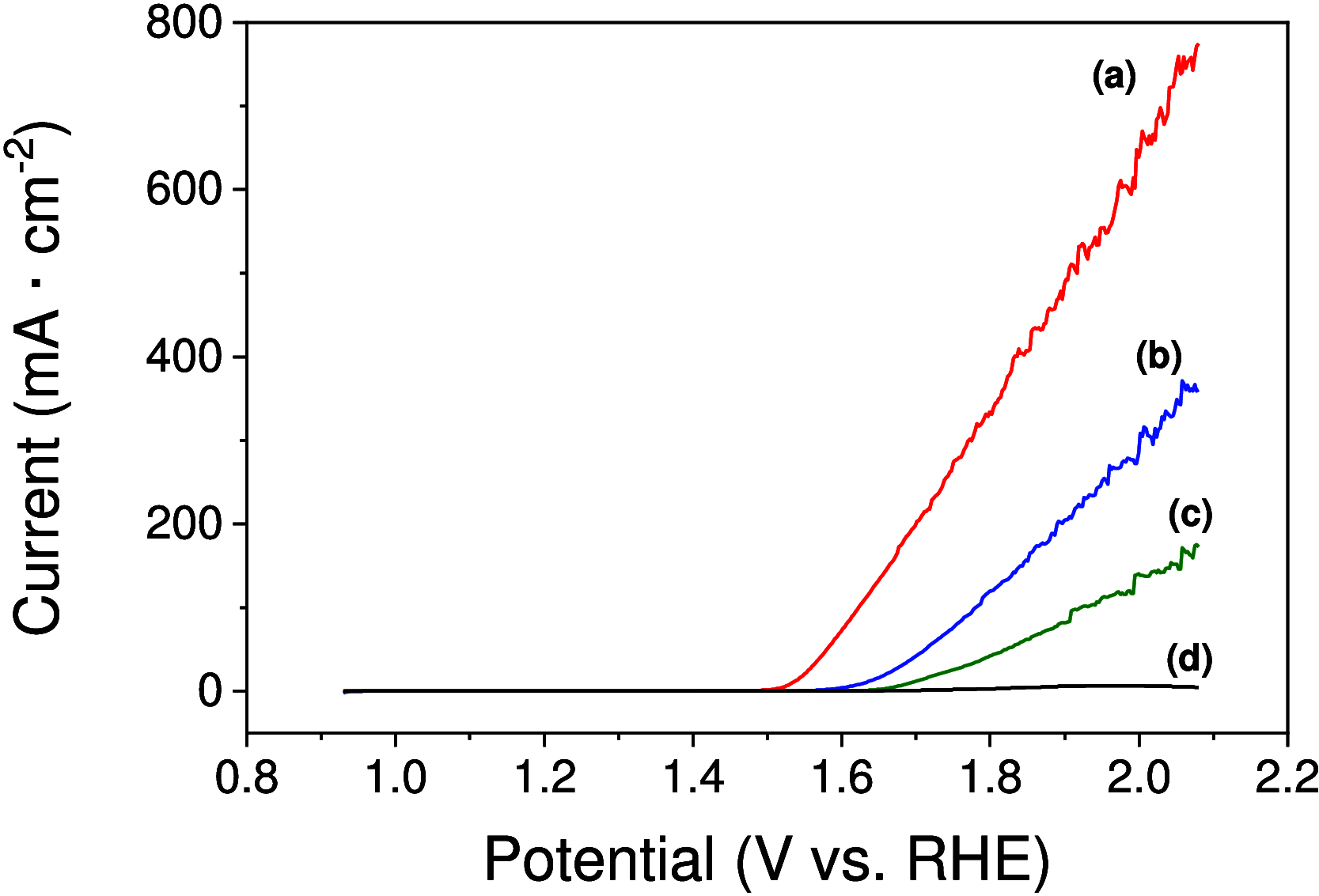
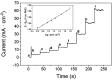
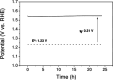
There is a great deal of interest in the development of electrocatalysts for the oxygen evolution reaction (OER) that are stable and have high activity because this anodic half-reaction is the main bottleneck in water splitting and other key technologies. Cobalt and iron oxide and oxyhydroxide electrocatalysts constitute a cheaper alternative to the highly active and commonly used Ir- and Ru-based catalysts. Most of the described electrocatalysts require tedious synthetic and expensive preparation procedures. We report here a facile and straightforward preparation of an electrocatalyst by a combination of commercial compounds, such as cobalt chloride and ferrocene. A highly active and stable OER electrocatalyst is obtained, which shows a low overpotential in the alkaline medium as a consequence of a synergistic effect between both compounds and is inexpensive.
Figures
References
-
- Kumar R., Singh R., Dutta S.. Review and outlook of hydrogen production through catalytic processes. Energy Fuels. 2024;38(4):2601–2629. doi: 10.1021/acs.energyfuels.3c04026. - DOI
-
- Zainal B. S., Ker P. J., Mohamed H., Ong H. C., Fattah I. M. R., Rahman S. M. A., Nghiem L. D., Mahlia T. M. I.. Recent advancement and assessment of green hydrogen production technologies. Renewable Sustainable Energy Rev. 2024;189:113941. doi: 10.1016/j.rser.2023.113941. - DOI
-
- Cho H. H., Strezov V., Evans T. J.. A review on global warming potential, challenges and opportunities of renewable hydrogen production technologies. Sustainable Materials and Technologies. 2023;35:e00567. doi: 10.1016/j.susmat.2023.e00567. - DOI
-
- Kaur M., Pal K.. Review on hydrogen storage materials and methods from an electrochemical viewpoint. Journal of Energy Storage. 2019;23:234–249. doi: 10.1016/j.est.2019.03.020. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

