Chemotherapy in older patients with early breast cancer
- PMID: 39405593
- PMCID: PMC11752109
- DOI: 10.1016/j.breast.2024.103821
Chemotherapy in older patients with early breast cancer
Abstract
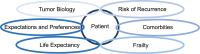
The incidence of breast cancer increases with age. Particularly in ageing societies, breast cancer has a significant impact on both the older patient and the healthcare system. In older patients with early breast cancer, there is a complex interplay between (i) tumor biology, (ii) risk of recurrence, (iii) comorbidities, (iv) frailty, (v) life expectancy and (vi) patient expectations and preferences. Our treatment guidelines are often based on large meta-analyses that have shown that (neo)adjuvant chemotherapy improves the survival rate in early breast cancer in general. This is particularly important in triple-negative and HER2-positive breast cancer, but hormone receptor (HR)-positive, HER2-negative patients with a higher risk of recurrence also benefit from chemotherapy. However, most studies included younger and carefully selected patients. Since there is a positive correlation between age and estrogen receptor status, as well as between age and the number of concomitant diseases and the tolerability of chemotherapy, it is of great importance to evaluate the effects of additional (neo)adjuvant chemotherapy, especially in older patients with early-stage breast cancer. There are only a few studies in which only older patients with early breast cancer were included. On the whole, they show that older patients with HR-positive, HER2-negative tumors hardly benefit from chemotherapy in addition to endocrine therapy. In these patients, additional chemotherapy should be considered critically when weighing up the potential benefits and harms. However, this critical evaluation should not be confused with abandoning standard chemotherapy when it is feasible and clinically indicated based on geriatric assessment, risk assessment, and patient preference. The aim of our narrative review is to provide a concise overview of the evidence on chemotherapy in older women with breast cancer and place it in the context of geriatric assessment and risk evaluation in older HR-positive, HER2-negative patients with early breast cancer. This in turn should help to critically weigh up the risks and benefits of chemotherapy for the individual older patient with early-stage breast cancer, which should ultimately lead to more individualized and at the same time more evidence-based treatment recommendations that take into account the complex interplay of different and sometimes contradictory patient- and tumor-specific factors.
Keywords: Chemotherapy; Early breast cancer; Estrogen receptor; Geriatric assessment; Older patients.
Copyright © 2024 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest MS reports grants and personal fees from Pierre-Fabre, grants, personal fees and non-financial support from Roche, grants, personal fees and non-financial support from Pfizer, grants and personal fees from Novartis, grants and personal fees from Astra-Zeneca, grants and personal fees from Eisai, personal fees from Amgen, grants, personal fees and non-financial support from Pantarhei Bioscience, grants, personal fees and non-financial support from BioNTech, grants from Genentech, personal fees from SeaGen, personal fees from Lilly, personal fees from Gilead, personal fees from Daiichi Sankyo, personal fees from Menarini Stemline, outside the submitted work; In addition, Dr. Schmidt has a patent EP: 2951317 Method for predicting the benefit from inclusion a taxane in a chemotherapy regimen in patients with breast cancer issued, and a patent EP2390370 A method for predicting the response of a tumor in a patient suffering from or at risk of developing recurrent gynecologic cancer towards a chemotherapeutic agent issued. SL reports employment as Chief Executive Officer (CEO) at German Breast Group (GBG) Forschungs GmbH; institutional fees for advisory board membership for AbbVie, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Bristol Myers Squibb (BMS), Celgene, DSI, EirGenix, Gilead, GSK, Lilly, Merck, Novartis, Olema, Pfizer, Pierre Fabre, Relay Therapeutics, Roche, Sanofi and Seagen; institutional fees as an invited speaker for AstraZeneca, DSI, Gilead, Medscape, Novartis, Pfizer, Roche, Seagen and Stemline-Menarini; institutional research grants from AstraZeneca, Celgene, Daiichi Sankyo, Immunomedics/Gilead, Novartis, Pfizer and Roche; institutional funding from AbbVie, Greenwich Life Sciences and Molecular Health; institutional licensing fees from VMscope GmbH; a role as a steering committee member (non-financial interest) for AstraZeneca, Daiichi Sankyo, Immunomedics/Gilead, Novartis, Pfizer, Roche and SeaGen; a role as a principal investigator (PI) for Pfizer (non-financial interest); a non-remunerated advisory role for Arbeitsgemeinschaft Gynäkologische Onkologie (AGO) Kommission Mamma; a non-remunerated role as PI for PI Aphinity; non-remunerated membership of Die AGO, the American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO), German Cancer Society (DKG), ESMO and the ESMO Guidelines Committee; non-remunerated role as Chair of ESMO Breast; institutional patents for EP19808852.8, EP14153692.0, EP21152186.9 and EP15702464.7 (non-financial interest).
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous