Altered brain complexity in first-episode antipsychotic-naïve patients with schizophrenia: A whole-brain voxel-wise study
- PMID: 39406039
- PMCID: PMC11525771
- DOI: 10.1016/j.nicl.2024.103686
Altered brain complexity in first-episode antipsychotic-naïve patients with schizophrenia: A whole-brain voxel-wise study
Abstract
Background: Measures of cortical topology are believed to characterize large-scale cortical networks. Previous studies used region of interest (ROI)-based approaches with predefined templates that limit analyses to linear pair-wise interactions between regions. As cortical topology is inherently complex, a non-linear dynamic model that measures the brain complexity at the voxel level is suggested to characterize topological complexities of brain regions and cortical folding.
Methods: T1-weighted brain images of 150 first-episode antipsychotic-naïve schizophrenia (FES) patients and 161 healthy comparison participants (HC) were examined. The Chaos analysis approach was applied to detect alterations in brain structural complexity using the largest Lyapunov exponent (Lambda) as the key measure. Then, the Lambda spatial series was mapped in the frequency domain using the correlation of the Morlet wavelet to reflect cortical folding complexity.
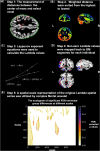
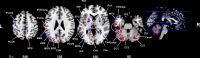
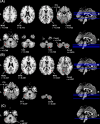
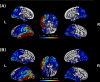
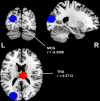
Results: A widespread voxel-wise decrease in Lambda values in space and frequency domains was observed in FES, especially in frontal, parietal, temporal, limbic, basal ganglia, thalamic, and cerebellar regions. The widespread decrease indicates a general loss of brain topological complexity and cortical folding. An additional pattern of increased Lambda values in certain regions highlights the redistribution of complexity measures in schizophrenia at an early stage with potential progression as the illness advances. Strong correlations were found between the duration of untreated psychosis and Lambda values related to the cerebellum, temporal, and occipital gyri.
Conclusions: Our findings support the notion that defining brain complexity by non-linear dynamic analyses offers a novel approach for identifying structural brain alterations related to the early stages of schizophrenia.
Keywords: Brain complexity; Cortical topology; Largest Lyapunov exponent; Non-linear dynamic model; Schizophrenia.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
References
-
- Breakspear M. The nonlinear theory of schizophrenia. Aust. N. Z. J. Psychiatry. 2006;40(1):20–35. - PubMed
-
- Chen Y., Pham T.D. Sample entropy and regularity dimension in complexity analysis of cortical surface structure in early Alzheimer's disease and aging. J. Neurosci. Methods. 2013;215(2):210–217. - PubMed
-
- Cuadra M.B., Cammoun L., Butz T., Cuisenaire O., Thiran J.P. Comparison and validation of tissue modelization and statistical classification methods in T1-weighted MR brain images. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging. 2005;24(12):1548–1565. - PubMed
-
- Dahnke R., Yotter R.A., Gaser C. Cortical thickness and central surface estimation. Neuroimage. 2013;65:336–348. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

