AKR1B1-dependent fructose metabolism enhances malignancy of cancer cells
- PMID: 39406918
- PMCID: PMC11618507
- DOI: 10.1038/s41418-024-01393-4
AKR1B1-dependent fructose metabolism enhances malignancy of cancer cells
Abstract
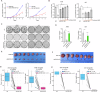
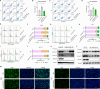
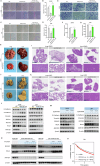
Fructose metabolism has emerged as a significant contributor to cancer cell proliferation, yet the underlying mechanisms and sources of fructose for cancer cells remain incompletely understood. In this study, we demonstrate that cancer cells can convert glucose into fructose through a process called the AKR1B1-mediated polyol pathway. Inhibiting the endogenous production of fructose through AKR1B1 deletion dramatically suppressed glycolysis, resulting in reduced cancer cell migration, inhibited growth, and the induction of apoptosis and cell cycle arrest. Conversely, the acceleration of endogenous fructose through AKR1B1 overexpression has been shown to significantly enhance cancer cell proliferation and migration with increased S cell cycle progression. Our findings highlight the crucial role of endogenous fructose in cancer cell malignancy and support the need for further investigation into AKR1B1 as a potential cancer therapeutic target.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

