Looking Beyond the Surface: Olutasidenib and Ivosidenib for Treatment of mIDH1 Acute Myeloid Leukemia
- PMID: 39406957
- PMCID: PMC11541360
- DOI: 10.1007/s11864-024-01264-7
Looking Beyond the Surface: Olutasidenib and Ivosidenib for Treatment of mIDH1 Acute Myeloid Leukemia
Abstract
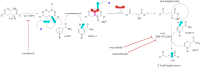
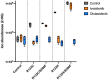
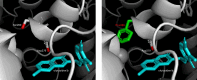
Mutations in isocitrate dehydrogenase-1 (IDH1) are recurrent in several malignancies and prevalent in acute myeloid leukemia (AML). Olutasidenib and ivosidenib are inhibitors that target mutant IDH1 (mIDH1) and are FDA approved for the treatment of patients with mIDH1 AML. Olutasidenib and ivosidenib were identified through unique molecular screens and thus are structurally very different molecules. A difference in clinical outcomes has been observed with olutasidenib, which has a longer duration of response than ivosidenib, despite similar rates of response being achieved with the two drugs, such as complete remission (CR) or CR with partial hematologic recovery (CR/CRh). In the absence of a head-to-head trial, this review examines both the extent of differences in clinical outcomes with the two drugs and provides the first comparison of the unique molecular and mechanistic features of each drug, such as molecular structure and binding kinetics, that may contribute to the observed clinical difference in outcomes. Olutasidenib is structurally smaller with a lower molecular weight than ivosidenib (FW 355 vs FW 583) and thus occupies less space in the binding pocket of IDH1 dimers, making it resistant to displacement by IDH1 second-site mutations. In biochemical studies, olutasidenib selectively inhibits mutant but not wild-type IDH1, whereas ivosidenib appears to potently block both mutant and wild-type IDH1. Although they have the same target, olutasidenib and ivosidenib have unique molecular features, which may translate to selectivity differences in their inhibitory activity against IDH1.
Keywords: 2-hydroxyglutarate; Alpha-ketoglutarate; Isocitrate dehydrogenase; Mutant IDH1.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
J.M.W. received consulting fees and/or participated in advisory boards for Rigel, Servier, BMS, Daiichi-Sankyo, Aptose, and Ativarre; S.J.S. was an employee and shareholder of Rigel Pharmaceuticals, Inc. at the time of manuscript drafting; B.A.J. served in a consultancy/advisory role for AbbVie, Bristol Myers Squibb, Daiichi Sankyo, Genentech, Gilead, GlycoMimetics, Kymera, Kura, Rigel, Schrodinger, Servier, Syndax and Treadwell, on a protocol steering committee for GlycoMimetics, on a data monitoring committee for Gilead, received travel reimbursement from AbbVie and Rigel, research funding to institution from AbbVie, Amgen, Aptose, AROG, Biomea, Bristol Myers Squibb, Celgene, Daiichi Sankyo, F. Hoffmann‑La Roche, Forma, Forty‑Seven, Genentech/Roche, Gilead, GlycoMimetics, Hanmi, Immune‑Onc, Incyte, Jazz, Kymera, Loxo, Pfizer, Pharmacyclics, Sigma Tau, and Treadwell.
Figures
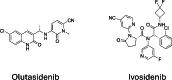
References
-
- Cortes JE. Olutasidenib: a novel mutant IDH1 inhibitor for the treatment of relapsed or refractory acute myeloid leukemia. Expert Rev Hematol. 2024:1–11. 10.1080/17474086.2024.2354486. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

